Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Book Solutions Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between the nature of n-bonds present in H3PO3 and HNO3 molecules?
Answer:
In H3PO3, there is pπ-dπ bond whereas in HNOs there is pπ-pπ bond.
Question 2.
Complete the following equations:
(i) PCl3 + H2O →
(ii) XeF2 + PF5 →
![]()
Answer:
(i) PCl3 + 3H2O → H3PO3 + 3HCl
(ii) XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+ [PF6]–
![]()
Question 3.
Which allotrope of sulphur is thermally stable at room temperature?
Answer:
Rhombic sulphur
![]()
Question 4.
O—O bond has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than S—S bond. Why?
Answer:
Due to smaller size the lone pairs of electrons on the O atom repel the bond pair of O—O bond to a greater extent as compared to the lone pairs of electrons on S atom in S—S bond. Consequently O—O bond has lower bond dissociation enthaltpy than S—S bond.
Question 5.
How would you account for the following:
(i) H2S is more acidic than H2O.
(ii) Both O2 and F2 stabilise higher oxidation states hut the ability of oxygen to stabilise the higher oxidation state exceeds that of fluorine.
Answer:
(i) This is because bond dissociation enthalpy of H—S bond is lower than that of H—O bond.
(ii) This is due to tendency of oxygen to form multiple bonds with metal atom.
Question 6.
Why solid PCl5 is ionic in nature?
Answer:
Because in solid state, PCl5 exists as [PCl4]+[PCl6]– and conducts electricity on melting.
![]()
Question 7.
On adding NaOH to ammonium sulphate, a colourless gas with pungent odour is evolved which form a blue coloured complex with Cu2+ ion. Identify the gas.
Answer:
Ammonia (NH3).
Question 8.
N2O5 is more acidic thanNaO3. Why?
Answer:
N2O5 is the anhydride of nitric acid, forms the stable acid with water as follows :
![]()
While N2O3 is the anhydride of nitrous acid, HNO2. It dissolves in water to form the unstable acid as follows :
![]()
Hence, N2O5 is more acidic thanN2O3.
Question 9.
Why is nitric oxide paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtained on cooling is diamagnetic?
Answer:
In gaseous state, NO2 exists as monomer which has one unpaired electron but in solid state, it dimerises to NO2 so no unpaired electron is left hence, the solid formed is diamagnetic.
![]()
Question 10.
In the preparation of H2SO4 by contact process, why is SO3 not absorbed directly in water to form H2SO4 ?
Answer:
Acid fog is formed, which is difficult to condense.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Account for the following:
(i) Bi(V) is a stronger oxidising agent than Sb(V).
(ii) N—N single bond is weaker than P—P single bond.
Answer:
(i) Due to inert pair effect +3 oxidation state of Bi is more stable than its +5 oxidation state while +5 oxidation state of Sb is more stable than its +3 oxidation state. Therefore, Bi (V) can accept a pair of electrons to form more stable Bi (III) more easily than Sb (V). Hence, Bi (V) is a stronger oxidising agent than Sb (V).
(ii) N—N single bond is weaker than P—P single bond due to large interelectronic repulsion between the lone pairs of electrons present on the N atoms of N—N bond having small bond length.
Question 2.
Account for the following:
(i) PCl5 is more covalent than PCl3.
(ii) Iron on reaction with HCl forms FeCl2 and not FeCl3.
(iii) The two O—O bond lengths in the ozone molecule are equal.
Answer:
(i) The oxidation state of central atom, i.e., phosphorus is +5 in PCl5 whereas it is +3 in PCl3. Higher the positive oxidation of central atom, more will be its polarising power which, in turn, increases the covalent character of bond formed between the central atom and the atoms surrounding it.
(ii) Iron reacts with HCl to form FeCl2 and H2.
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2
H2 thus produced prevents the oxidation of FeCl2 to FeCl3.
(iii) Ozone is a resonance hybrid of the following two main structures :
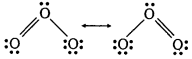
As a result of resonance, the two O—O bond lengths in O3 are equal.
![]()
Question 3.
How would you account for the following:
(i) The electron gain enthalpy with negative sign is less for oxygen than that for sulphur.
(ii) Fluorine never acts as the central atom in polyatomic interhalogen compounds.
Answer:
(i) This is due to smaller size of oxygen the electron cloud is distributed over a small region of space, making electron density high which repels the incoming electrons.
(ii) Fluorine never acts as the central atom in polyatomic interhalogen compounds since it is the most electronegative element of the group.
Question 4.
PCl5 reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver salt is obtained, which dissolves on adding excess aqueous NH3 solution. Write the reactions involved to explain what happens.
Answer:
PCl5 on reaction with finely divided silver produced silver halide.
PCl5 + 2Ag → 2AgCl + PCl3
AgCl on further reaction with aqueous ammonia solution produces a soluble complex of [Ag(NH3)2]+Cl–.
![]()
Question 5.
Account for the following:
(i) Sulphur in vapour state exhibits paramagnetism.
(ii) H3PO2 is a stronger reducing agent than H3PO2.
Answer:
(i) In vapour form, sulphur partly exists as S2 molecules which have two unpaired electrons in the antibonding n molecular orbitals like 02 molecule and hence, exhibits paramagnetism.
(ii) Acids which contain P—H bonds, have reducing character. Since, H3PO2 contains two P—H bonds while H3PO3 contains only one P—H bond, therefore H3PO2 is a stronger reducing agent than H3PO3.
![]()
Question 6.
What happens when:
(i) ortho phosphorus acid is heated?
(ii) XeF6 undergoes complete hydrolysis?
Answer:
(i) On heating, ortho phosphorus acid disproportionates to give orthophosphoric acid and phosphine gas.
![]()
(ii) When XeF6 undergoes complete hydrolysis, it forms XeO3.
XeF6 + 3H2O → 6HF + XeO3
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(a) Account for the following:
(i) Acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) There is large difference between the melting and boiling points of oxygen and sulphur.
(iii) Nitrogen does not form pentahalide.
(b) Draw the structures of the following:
(i) ClF3
(ii) XeF4
Answer:
(a) (i) As the size of halogen atom increases from F to I, the bond dissociation enthalpy of H—X bond decreases from H—F to H—I. Due to this, acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) Because of small size and high electronegativity oxygen forms pπ-pπ multiple bonds and exists as a diatomic, O2 molecule. The molecules are held together by weak van der Waal forces. Sulphur on the other hand due to its higher tendency for catenation and lower tendency for pπ-pπ multiple bond formation, forms octa-atomic, S8 molecule. Because of bigger size of S8 molecule than O2 molecule the force of attraction holding the S8 molecules together are much stronger than O2 molecules. Hence, there is large difference between the melting and boiling points of oxygen and sulphur.
(iii) Nitrogen with n = 2, has s and p-orbitals only. It does not have d-orbitals to expand its covalency beyond four. Due to this, it does not form pentahalide.
(b)
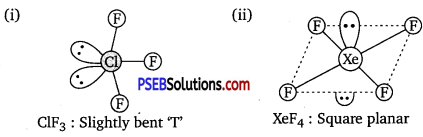
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Bond enthalpy of F2 is lower than that of Cl2.
(ii) PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3.
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules :
(i) BrF3
(ii)BrF5
(iii) (HPO3)3
Answer:
(a) (i) Bond dissociation enthalpy decreases as the bond distance increases from F2 to I2 because of the corresponding increase in the size of the atom as we move from F to I. The F—F bond dissociation enthalpy is, however, smaller than that of Cl—Cl and even smaller than that of Br—Br. This is because F atom is very small and hence the three lone pairs of electrons on each F atom repel the bond pair holding the F-atoms in F2 molecule resulting lower bond enthalpy than Cl2.
(ii) Unlike NH3, PH3 molecules are not associated through hydrogen bonding in liquid state. That is why the boiling point of PH3 is lower than NH3.
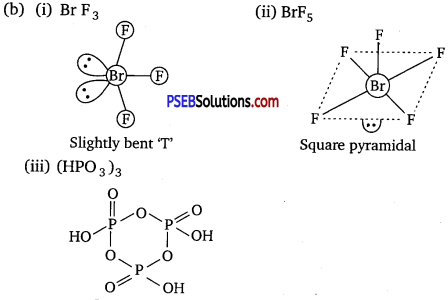
Question 3.
(a) Complete the following chemical reaction equations:
(i) AgCl(s) + NH3 (aqr) →
(ii) P4(s) + NaOH(aq) + H2O(l) →
(b) Explain the following observations :
(i) H2S is less acidic than H2Te.
(ii) Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine.
(iii) Noble gases are the least reactive elements.
Answer:
(a) (i) AgCl + 2NH3 → [Ag(NH3)2]+ Cl–
(ii) P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O → PH3 + 3NaH2PO2
(b) (i) This is because bond dissociation enthalpy of H—Te bond is less than H—S as the size of Te is larger than S.
(ii) Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine due to low dissociation enthalpy of F—F bond and high hydration enthalpy of F– ions.
(iii) Noble gases are the least reactive elements due to fully filled outermost shells, high ionisation enthalpy and positive electron gain enthalpy.
![]()
Question 4.
(a) Arrange the following in the order of property indicated against each set:
(i) F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (increasing bond dissociation enthalpy)
(ii) H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te (increasing acidic character)
(b) A colourless gas ‘A’ with a pungent odour is highly soluble in water and its aqueous solution is weakly basic. As a weak base it precipitates the hydroxides of many metals from their salt solution. Gas ‘A* finds application in detection of metal ions. It gives a deep blue colouration with copper ions. Identify the gas A’ and write the chemical equations involved in the following :
(i) Gas ‘A’ with copper ions
(ii) Solution of gas ‘A’ with ZnSO4 solution.
Answer:
(a) (i) I2 < F2 < Br2 < Cl2
(ii) H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te
(b) The gas ‘A’ is ammonia (NH3).
(i) Cu2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) ⇌ [Cu(NH3)4]2+(aq)
(ii) ZnSO4(aq) + 2 NH4OH(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) + (NH4) 2 SO4(aq)
Question 5.
Answer the following questions
(a) Write the formula of the neutral molecule which is isoelectronic with ClO–.
(b) Draw the shape of H2S2O7.
(c) Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with P4. Write the formula of the stable molecule formed when this oxide undergoes dimerisation.
(d) Bleaching action of chlorine is permanent. Justify.
(e) Write the disproportionation reaction of that oxoacid of nitrogen in which nitrogen is in + 3 oxidation state.
Answer:
(a) ClF
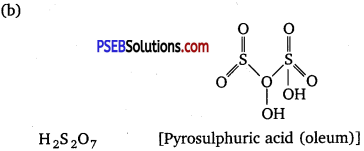
(c) N2O4
(d) Bleaching action of chlorine is permanent due to oxidation.
Cl + H2O → 2HCl + [O]
(d) 3HNO2 → HNO3 + H2O + 2NO