Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements Important Questions
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the formula of kemite, an ore of boron?
Answer:
Formula of kernite, Na2[B4O5(OH)4] or Na2B4O7.2H2O
Question 2.
Complete the following chemical equations :
Z + 3LiAlH4 → X + 3LiF + 3AlF3
X + 6H2O → Y + 6H2
X + 3O2 → B2O3 + 3H2O
Answer:
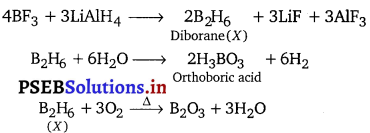
![]()
Question 3.
Tl(NO3)3 acts as an oxidising agent. Explain.
Answer:
Due to inert pair effect, Tl in +1 oxidation state is more stable than that of +3 oxidation state. Therefore, Tl(NO3)3 acts as an oxidising agent and readily reduced to TlNO3.
Question 4.
Why is B—X bond distance in BX3 shorter than the theoretically expected value?
Answer:
This is due to pπ—pπ back bonding of the completely filled p-orbital of halogen X into the empty p-orbital of boron.
Question 5.
Are all the B—H bonds in diborane equivalent?
Answer:
No, there are two types of bonds in diborane two electron normal bonds and three centred two electron bonds.
Question 6.
Name the member of group 14 that forms the most acidic oxide.
Answer:
Among monoxides, CO is neutral and GeO is acidic while among dioxides, CO2, SiO2 are acidic, GeO2 is also acidic but less acidic than Si02.
Question 7.
Silicones are used for making waterproof fabrics. Give reason.
Answer:
Silicones are synthetic polymers containing repeated units of R2SiO where R is alkyl group.
Therefore, these are water repellants i.e., do not absorb water and are used for making waterproof fabrics.
Question 8.
Atomic radius of gallium (135 pm) is less than that of aluminium (143 pm).
Answer: It is due to poor shielding effect of 3d-electrons due to which effective nuclear charge increases in Ga, therefore, it is smaller than Al.
Question 9.
AlF3 is high melting solid but AlCl3 is low melting. Explain.
Answer: AlF3 is high melting solid because it is ionic in nature. On the other hand, A1C13 is covalent in nature and hence is a low melting solid.
Question 10.
How will you prepare an ahuninosilicate?
Answer:
Aluminosilicate is prepared by substituting some of the Si atoms in the three dimensional network of SiO2 by Al atoms.
![]()
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Like CO, why its analog of SiO is not stable?
Answer:
CO is a resonance hybrid of the following two structures :
![]()
Thus, CO contains pπ-pπ multiple bonds. This is due to the reason that carbon has a strong tendency to form pπ—pπ multiple bonds due to its small size and high electronegativity. Silicon, on the other hand, because of its _ bigger size and lower electronegativity has no tendency to form pπ—pπ multiple bonds and hence, Si does not form SiO molecule analogous to CO molecule.
Question 2.
Account for the following:
(i) Graphite is used as lubricant.
(ii) Diamond is used as an abrasive.
Answer:
(i) Graphite has layered structure. Layers are held together by weak van der Waals’ forces and hence can be made to slip over one another. Therefore, graphite acts as a dry lubricant.
(ii) In diamond, each sp3 hybridised carbon atom is linked to four other carbon atoms. It has three-dimensional network of carbon atoms. It is very difficult to break extended covalent bonding and therefore diamond is a hardest substance on the earth. That’s why it is used as an abrasive.
Question 3.
Which one is more soluble in diethyl ether, anhydrous AlCl3 or hydrated AlCl3? Explain in terms of bonding.
Answer:
Anhydrous AlCl3 is an electron-deficient compound while hydrated AlCl3 is not. Therefore, anhydrous A1C13 is more soluble in diethyl ether because the oxygen atom of ether donates a pair of electrons to the vacant p-orbital on the Al atom in AlCl3 forming a coordinate bond.
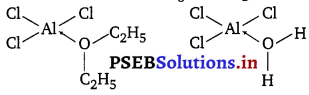
In case of hydrated AlCl3, Al is not electron deficient since H2O has already donated a pair of electrons to it.
Question 4.
BCl3 is trigonal planar while AlCl3 is tetrahedral in dimeric state. Explain.
Or
BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised through halogen bridging. Give reason. Explain the structure of the dimer of AlCl3 also.
Answer:
Both BCl3 and AlCl3 are electron deficient molecules having six electrons in the valence shell of their respective central atoms. To complete their octets, the central atom in each case can accept a pair of electrons from the chlorine atom of another molecule forming dimeric structures. However, because of small size of B, it cannot accommodate four big sized Cl atoms around it. Therefore, BCl3 prefers to exist as a monomeric planar molecule in which B atom is sp2 -hybridised.
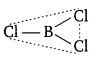
On the other hand, Al because of its bigger size can easily accommodate four Cl atoms around it. As a result, AlCl3 exists as a dimer. In this dimer, since the covalency of Al has increased to 4.
Therefore, Al is sp3-hybridised and the four Cl atoms are held tetrahedrally around it.
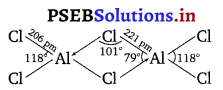
![]()
Question 5.
Three pairs of compounds are given below. Identify that compound in each of the pairs which has group 13 element in more stable oxidation state. Give reason for your choice. State the nature of bonding also.
(i) TICl3, TlCl
(ii) AlCl3, AlCl
(iii) InCl3, InCl
Answer:
(i) Due to strong inert pair effect, +1 oxidation state of T1 is more stable than +3. Since, compounds in lower oxidation state are ionic but covalent in higher oxidation state, therefore, TlCl3 is less stable and covalent in nature but TlCl is more stable and is ionic in nature.
(ii) Due to absence of d-orbitals, Al does not show inert pair effect. Therefore, it is most stable than A1C1. Further, in the solid or the vapour state, AlCl3 is covalent in nature but in aqueous solution, it ionises to form Al3+ (aq) and Cl–(aq) ions.
(iii) Due to inert pair effect, indium exists in both +1 and +3 oxidation states, out of which +3 oxidation state is more stable than +1 oxidation
state. In other words, InCl3 is more stable than InCl. Being unstable, InCl undergoes disproportionation reactions.
3InCl(aq) → 2In(s) + In3+(aq) + 3Cl– (aq)
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(i) What are silicones? State the uses of silicones.
(ii) What are boranes? Give chemical equation for the preparation of diborane.
Answer:
(i) Silicones are a group of organosilicon polymers, which have (R2SiO) as a repeating unit. These may be linear silicones, cyclic silicones and cross-linked silicones. These are prepared by the hydrolysis of alkyl or aryl derivatives of SiCl4 like RSiCl3, R2SiCl2 and R3SiCl and polymerisation of alkyl or aryl hydroxy derivatives obtained by hydrolysis.
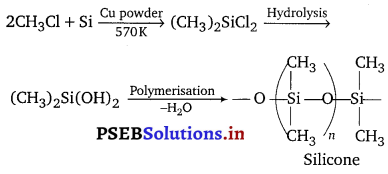
Uses : These are used as sealant, greases, electrical insulators and for water proofing of fabrics. These are also used in surgical and cosmetic plants.
(ii) Boron forms a number of covalent hydrides with general formulae BnHn+4 and BnHn+6. These are called boranes. B2H6 and B4H10 are the representative compounds of the two series respectively.
Preparation of diborane : It is prepared by treating boron trifluoride with LiAlH4 in diethyl ether.
4BF3 + 3LiAlH4 → 2B2H6 + 3LiF + 3AlF3
On industrial scale it is prepared by the reaction of BF3 with sodium hydride.
![]()
![]()
Question 2.
Account for the following observations :
(i) AlCl3 is a Lewis acid.
(ii) Though fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine yet BF3 is weaker Lewis acid than BCl3.
(iii) PbO2 is stronger oxidising agent than SnO2.
(iv) The +1 oxidation state of thallium is more stable than its +3 state.
(i) In AlCl3, Al has only six electrons in its valence shell. It is an electron deficient species. Therefore, it acts as a Lewis acid (electron acceptor).
(ii) In BF3, boron has a vacant 2p-orbital and fluorine has one 2p completely filled unutilized orbital. Both of these orbitals belong to same energy level therefore, they can overlap effectively and form pπ—pπ bond. This type of bond formation is known as back bonding. While back bonding is not possible in BCl3 because there is no effective overlapping between the 2p-orbital of boron and 3p-orbital of chlorine. Therefore, electron deficiency of B is higher in BCl3 than that of BF3. That’s why BF3 is a weaker Lewis acid than BCl3.
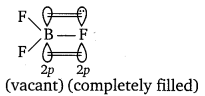
(iii) Pb4+ is less stable thanPb2+, due to inert pair effect therefore, Pb4+ salts act as strong oxidising agents. Sn2+ is also less stable than Sn4+, thus Sn4+ can also act as an oxidising agent. But Pb4+ is a stronger oxidising agent than Sn4+ because inert pair effect increases down die group.
(iv) Tl+ is more stable than Tl3+ because of inert pair effect.