Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 15 Our Environment Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Our Environment
PSEB 10th Class Science Guide Our Environment Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following groups contains only biodegradable items :
(A) Grass, flowers and leather
(B) Grass, wood and plastic
(C) Fruit-peels, cake and lime-juice
(D) Cake, wood and grass.
Answer:
(A), (C) and (D) groups.
Question 2.
Which of the following constitute a food chain?
(A) Grass, wheat and mango
(B) Grass, goat and human
(C) Goat, cow and elephant
(D) Grass, fish and goat.
Answer:
(B) Grass, goat and human.
Question 3.
Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
(A) Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping
(B) Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
(C) Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter
(D) All of the above.
Answer:
(D) All of the above.
Question 4.
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer:
- If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, imbalances will be created in the food chain.
- The population of organisms in pervious trophic level will increase. If we kill population of frogs in the following food chain, the population of insects will increase to a great level and in turn they will damage the green plants.
Green plants → Insects → Frog - The population of organisms in the next trophic level will decrease.
Question 5.
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer:
- If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, imbalances will be created in the food chain.
- The population of organisms in pervious trophic level will increase. If we kill population of frogs in the following food chain, the population of insects will increase to a great level and in turn they will damage the green plants.
Green plants → Insects → Frog - The population of organisms in the next trophic level will decrease..
![]()
Question 6.
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Or
What is biological magnification? What are its effects?
Answer:
Biological magnification. The phenomenon in which the harmful pollutants (such as pesticides) enter the food chain and get concentrated more and more at each successive trophic level of organisms is called biological magnification.
The level of biological magnification will be different at different trophic levels of the ecosystem.
This can be illustrated by the following example :
A large number of toxic chemicals like pesticides, weedicides, insecticides and fungi-cides are used to protect the crop plants from pests and diseases. Some of these chemi-cals get mixed up with the soil whereas others get washed down into the surface water bodies like ponds, rivers, etc., and the underground water bodies.
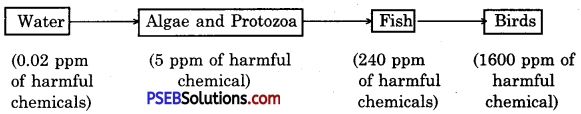
Water in a pond, lake or river contain only a small amount (0.02 ppm) of the harmful chemicals. The algae (phytoplankton) and protozoa (zooplankton) which utilize this wa-ter, contain a higher proportion (5 ppm). The fish which feeds on these organisms has a still higher amount of chemicals (240 ppm.) Birds which feed on these fish contain the highest amount (1600 ppm).
Therefore, we observe that as we go higher and higher in the food chain, the concentration of pesticides in the body of the organisms gradually increases. For example, in the above cited example, the biological magnification of harmful pesticides goes up to 8000 times from water to fish eating birds.
Effects of biological magnification. This is the reason why our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetable and fruits and even meat contain varying amounts of pesticides residues. So, the highest trophic level at the extreme right of food chain has the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in a food-chain.
Question 7.
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Or
Explain two ways in which non-biodegradable substances affect our envi¬ronment.
Answer:
Problems caused by non-biodegradable wastes
- Non-biodegradable solid waste is a great environmental hazard.
- Plastic and their waste products such as carry bags, waste glasses, bottles, cups, plates are most dangerous. They choke in drain.
- They cause soil pollution and degrade the soil.
- They prevent growth of vegetation when dumped underground.
- Water pollution will make this water not fit for drinking.
- The plastic wastes when mixed with municipal waste make them unfit for recycling.
- Non-biodegradable substances may be inert and simply persist in the environment for a long time and may harm various members of the ecosystem.
Question 8.
If all the wastes we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the enviroment?
Answer:
If all the wastes are biodegradable they will help in maintaining a neat, clean and stable environment.
Question 9.
Why damage to the ozone layer is a cause of concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer:
Ozone layer absorbs ultraviolet radiation of the sunlight which is very harmful to human beings. If the ozone layer in the atmosphere is depleted, these radiations would reach the earth and would cause many damages such as skin cancer, genetic disorders in human and other living beings.
The steps taken to limit the damage of ozone layer are as follows :
- Judicious use of aerosol spray propellants such as fluorocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons which cause depletion or hole in ozone layer.
- Limited use of supersonic planes.
- Control over large scale nuclear explosions.
Science Guide for Class 10 PSEB Our Environment InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable?
Answer:
Some substances such as paper, clothes, vegetables, wood etc. can be broken down into simple substances by the action of living organisms or biological processes in nature are said to be biodegradable.
There are other substances such as metals, plastics etc. which cannot be broken down into simpler substances by the action of living organisms or biological processes are termed non-biodegradable substances.
Question 2.
Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
- Biodegradable substances get simplified by the action of micro-organisms and the simple components are restored to environment, organisms or biological processes.
- They help in recycling. Gobar gas plant is best example of recycling in which dung and faeces are utilized to produce gas for cooking and the remains form important manures.
- Organic matter of biodegradable substances cause the growth of mosquitoes, flies etc. which spread diseases.
Question 3.
Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
- The non-biodegradable substances add to the pollution.
- Biomagnification of pesticides such as D.D.T. in the body of living system is very harmful.
- Solid waste leads to generation of methane which is causing global warming.
Question 4.
What are trophic levels? Give an example of food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer:
Trophic levels. The various steps in a food chain where transfer of food (energy) takes place are called trophic levels. Producer formed by green plants form first trophic level in a food chain.
Food chain: It is a sequential list of one organism consuming the other.
A simplest form of food chain is represented as
Producer → Herbivore → Carnivore
Characters of food chain.
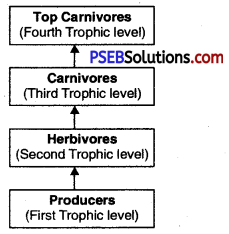
Topic levels-a food chain
- It is always straight.
- In shorter food chain, the greater is the available energy.
- The number of steps in any food chain is restricted to four or five.
- There is always unidirectional flow of energy in a food chain.
Question 5.
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
Answer:
These oganisms feed on the dead bodies of plants and animals. Bacteria, fungi and some lower invertebrates are examples of decomposer. They breakdown the organic components into simple inorganic molecules. They carry out natural process of decomposition. They return the simple components to soil and help in making the steady state of ecosystem. Decomposers are essential component of an ecosystem. They create a balance in the environment. They are called natural changing agents.
Question 6.
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Answer:
Ozone. Ozone is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen in the presence of
![]()
- Oxygen is essential for all aerobic forms of life but ozone is a deadly poison.
- Ozone is very poisonous at ground level. Ozone performs an important function at the higher level of the atmosphere.
- Ozone absorbs UV rays from the sun. Thus protects the living system on earth from any kind of damage.
![]()
Question 7.
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer:
- Recycling of wastes
- Reduction at source
- Better management
- Vermicomposting
- Use of eco-friendly products such as disposable paper cups in place of plastic cups.