Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.3
1. Draw a line r and mark a point P on it. Construct a line perpendicular to r at point P.
Question (i)
Using a ruler and compasses.
Solution:
Using ruler and compasses
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line r and mark a point P on it.
![]()
2. Draw an arc from P to the line r of any suitable radius which intersects line r at A and B.
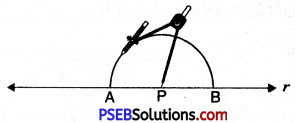
3. Draw arcs of any radius which is more than half of arc made in step (2) from A and B which intersect at Q.
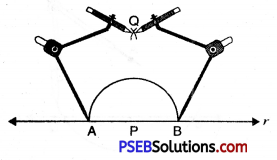
4. Join PQ.
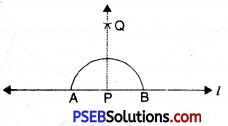
Thus PQ is perpendicular to AB or line l or PQ ⊥ A.
Here P is called foot of perpendicular.
![]()
Question (ii)
Using a ruler and a set square.
Solution:
Using a ruler and a set square
Steps of Construction
1. Draw a line r and a point P on it.
2. Place one of the edges of a ruler along the line l and hold if firmly.
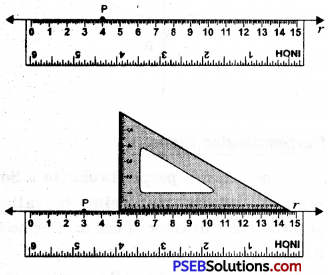
3. Place the set square in such a way that one of its edges contaning the right angle coincides with the ruler.
4. Holding the ruler, slide the set square along the line l till the vertical side reaches the point P.
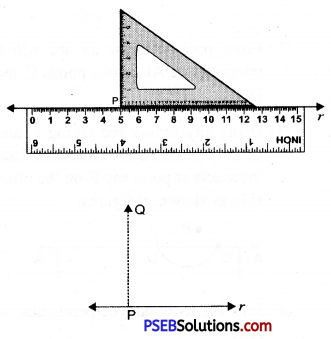
5. Firmly hold the set square in this position. Draw PQ along its vertical edge. Now PQ is the required perpendicular to l ie. PQ ⊥ r.
2. Draw a line p and mark a point z above it. Construct a line perpendicular to p, from the point z.
Question (i)
Using a ruler and compasses.
Solution:
1. Draw a line p and mark a point z not lying on it.
2. From point z draw an arc which intersects line p at two points P and Q.

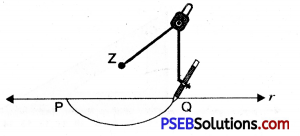
3. Using any radius and taking P and Q as centre, draw two arcs that intersect at point say B. On the other side (a shown in figure).
4. Join AB to obtain altitude to the line p.
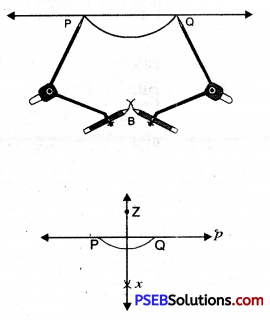
Thus xz is altitude to line p.
i.e. xz ⊥ p.
![]()
Question (ii)
Using a ruler and set square
Solution:
Steps of constructions:
1. Draw a line p and mark a point z which is not lying on it.
2. Place one of the edge of a ruler along the line p and hold it firmly.
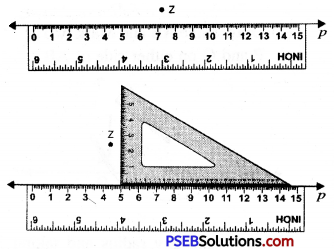
3. Place the set square in such a way that one of its edges containing the right angle coincides with the ruler.
4. Holding the ruler firmly, slide the set square along the line p till its vertical side reaches the point z.
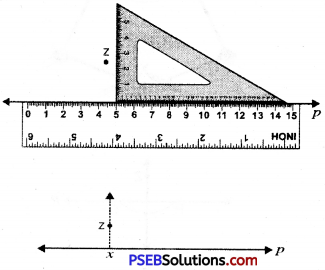
5. Firmly hold the set square in this position, Draw xz along its vertical edge. Now xz is the required altitude to p i.e. xz ⊥ p.
3. Draw a line AB and mark two points P and Q on either side of line AB, Construct two lines perpendicular to AB, from P and Q using a ruler and compasses.
Solution:
1. Draw a line AB and Mark two points P and Q on either side of AB.

2. From point P draw an arc which intersect line AB at two points C and D.
3. Using any radius and taking C and D as centre draw two arcs that intersects at point say E on the other side as shown in figures.

4. Join PE to obtain perpendicular to AB.
5. From point Q draw an arc which intersects AB at two points X and Y.
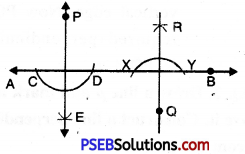
6. Using any radius and taking X and Y as centre draw two arcs that intersects at point say R on the other side of line AB as shown in figures.
7. Join QR to obtain perpendicular to AB.
Thus, PE ⊥ AB and QR ⊥ AB
![]()
4. Draw a line segment of 7 cm and draw perpendicular bisector of this line segment.
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment AB = 7 cm.
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw an arc on both sides of AB.
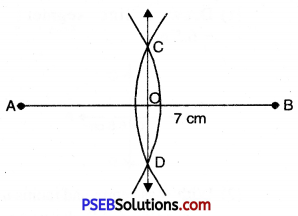
3. With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2, draw an arc intersecting the first arc at C and D.
4. Join CD intersecting AB at O. Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
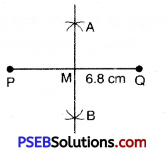
5. Draw a line segment PQ = 6.8 cm and draw its perpendicular bisector XY which bisect PQ at M. Find the length of PM and QM. Is PM = QM ?
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line segment PQ = 6.8 cm
2. With P as centre and radius more than half of PQ draw arcs on both sides of PQ.
![]()
3. Now with Q as centre and the same radius as in step 2 draw arcs intersecting the previous drawn arcs at A and B respectively.
4. Join AB intersecting PQ at M. Then M bisects the line segment.
5. Measure the length of PM and QM
PM = 3.4 cm and QM = 3.4 cm
∴ PM = QM.
![]()
6. Draw perpendicular bisector of line segment AB = 5.4 cm. Mark point X anywhere on perpendicular bisector Join X with A and B. Is AX = BX ?
Solution:
Steps of construction.
1. Draw a line segment AB = 5.4 cm.
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw an arc in both sides of AB.
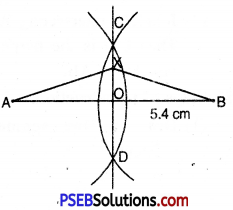
3. With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2, draw an arc intersecting the first arc at C and D.
4. Join CD intersecting AB at O.
Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Mark any point X on the perpendicular bisector CD. Drawn. Then join AX and BX.
On examination, we find that AX = BX.
7. Draw perpendicular bisectors of line segment of the following lengths.
Question (i)
8.2 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line regment AB = 8.2 cm
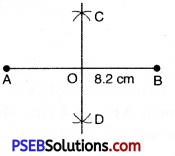
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw arcs on both sides of AB.
3. With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2, draw an arcs intersecting the previous arc at C and D.
4. Join CD intersecting AB at O. Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
![]()
Question (ii)
7.8 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line segment AB = 7.8 cm
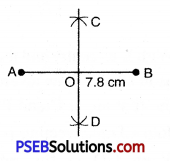
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB draw arcs on both sides of AB.
3. With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2, draw arcs intersecting the previous arcs at C and D.
4. Join CD intersecting AB at O. Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Question (iii)
6.5 cm.
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line segment AB = 6.5 cm
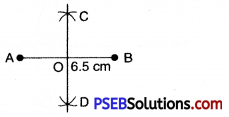
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB draw arcs on both sides of AB.
3. With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2 draw arcs intersecting the previous arcs at C and D.
4. Join CD intersecting AB at O. Then CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
![]()
8. Draw a line segment of length 8 cm and divide it into four equal parts Using compasses. Measure each part.
Solution:
Steps of construction.
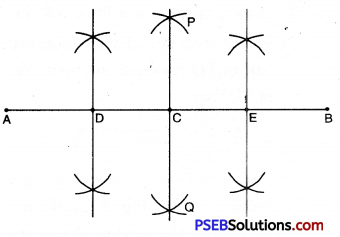
1. Draw a line segment AB of length 8 cm
2. With A as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw arcs on both sides of AB.
3. With B as centre and the same radius as in step 2, draw arcs intersecting the previous arcs at P and Q.
4. Join PQ intersecting AB at C then PQ is the perpendicular bisector of AB intersecting AB at C.
5. Similarly draw the perpendicular bisector of AC intersecting AC at D.
6. Draw the perpendicular bisector of CB intersecting CB at E.
By actual measurement, it can be verified that
AD = DC = CE = EB