Punjab State Board PSEB 4th Class Punjabi Book Solutions Chapter 19 ਬਾਬੇ ਭਕਨੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਪਿਆਰੀਆਂ ਗੱਲਾਂ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 4 Punjabi Chapter 19 ਬਾਬੇ ਭਕਨੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਪਿਆਰੀਆਂ ਗੱਲਾਂ
ਪਾਠ-ਅਭਿਆਸ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-ਉੱਤਰ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਬਾਬਾ ਸੋਹਣ ਸਿੰਘ ਭਕਨਾ ਕੌਣ ਸਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
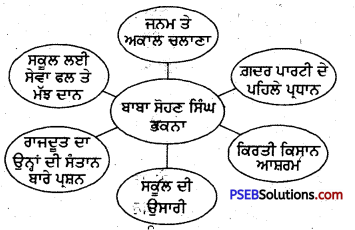
ਬਾਬਾ ਸੋਹਣ ਸਿੰਘ ਭਕਨਾ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਦੇਸ਼ਭਗਤ ਸਨ । ਆਪ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਵਿਚ ਭਾਰਤੀਆਂ ਵਲੋਂ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਲਈ ਬਣਾਈ ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੇ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਸਨ ਆਪ 26 ਸਾਲ ਜੇਲ੍ਹ ਵਿਚ ਰਹੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਬਾਬਾ ਸੋਹਣ ਸਿੰਘ ਭਕਨਾ ਨੇ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਆਸ਼ਰਮ ਖੋਲ੍ਹਿਆ ਤੇ ਕਿਉਂ ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਬਾਬਾ ਸੋਹਣ ਸਿੰਘ ਭਕਨਾ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਪਿੰਡ ਵਿਚ ਦੇਸ਼-ਭਗਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਪਾਲਣ-ਪੋਸ਼ਣ ਲਈ ਕਿਰਤੀ-ਕਿਸਾਨ ਆਸ਼ਰਮ ਖੋਲ੍ਹਿਆ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਰਾਜਦੂਤ ਨੇ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਤੋਂ ਕੀ ਪੁੱਛਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਕੀ ਉੱਤਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਰਾਜਦੂਤ ਨੇ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੂੰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਬਾਰੇ ਪੁੱਛਿਆ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਸਕੂਲ ਵਿਚ ਪੜ੍ਹਦੇ ਤਿੰਨ ਸੌ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੀ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਦੱਸਿਆ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਲੇਖ ਦੇ ਸੇਵਾ-ਫਲ ਦੇ ਪੈਸੇ ਕਿੱਥੇ ਖ਼ਰਚ ਕੀਤੇ ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੂੰ ਲੇਖ ਦੇ ਸੇਵਾ-ਫਲ ਦੇ ਪੈਸੇ ਗਰੀਬ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਰਦੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਬੂਟਾਂ ਉੱਤੇ ਖ਼ਰਚ ਕੀਤੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ: 5.
ਲੋਹੜੀ ਦੇ ਮੌਕੇ ‘ਤੇ ਮੱਝ ਦਾਨ ਕਰਨ ਸਮੇਂ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਮਾਤਾ ਜੀ ਨੂੰ ਕੀ ਕਿਹਾ ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਮੱਝ ਦਾਨ ਕਰਨ ਸਮੇਂ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਮਾਤਾ ਜੀ ਨੂੰ ਕਿਹਾ, “ਘਰ ਦੀ ਕਿਸੇ ਵੀ ਚੀਜ਼ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਸਕੂਲ ਕਿਤੇ ਚੰਗਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿੱਥੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਦਗੀ ਬਣਦੀ ਏ । ਇਹ ਮੱਝ ਸਕੂਲ ਨੂੰ ਦਾਨ ਦੇ ਦਿਓ।”
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਅੰਤਲੇ ਪਲਾਂ ਤਕ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਝੁੱਗੀਆਂ ਜਿਹੇ ਘਰ ਵਿਚ ਹੀ ਕਿਉਂ ਰਹੇ. ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਜਦ ਆਪਣਾ ਪੁਰਾਣਾ ਘਰ ਢਾਹ ਕੇ ਨਵਾਂ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਸ਼ਹਿਰੋਂ ਗਾਡਰ ਲੈਣ ਗਏ, ਤਾਂ ਰਸਤੇ ਵਿਚ ਟੱਪਰੀਵਾਸਾਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਝੁੱਗੀਆਂ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਨ ਪਿਘਲ ਗਿਆ ਉਹ ਸ਼ਹਿਰੋਂ ਗਾਡਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਥਾਂ ਬਾਂਸ ਤੇ ਸਿਰਕੀਆਂ ਲਿਆ ਕੇ ਭੁੱਗੀਆਂ ਜਿਹਾ ਘਰ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਰਹਿਣ ਲੱਗੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
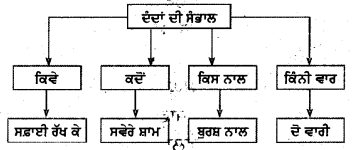
ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਿਹੜੀ ‘ਸਾਂਝੀ-ਵੰਡ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਖੁਸ਼ੀ ਹੋਈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਵਲੋਂ ਲਾਏ ਆਤੂ ਦੇ ਬੂਟੇ ‘ਤੇ ਇਕ ਆਤੂ ਲੱਗਾ ਪੱਕ ਜਾਣ ਤੇ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਉਸ ਆਤੂ ਨੂੰ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਭੋਰਾ-ਭੋਰਾ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਵੰਡਿਆ । ਇਸ “ਸਾਂਝੀ ਵੰਡ” ਵਿਚ ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਤੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਤ ਖੁਸ਼ੀ ਹੋਈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਬੈਕਟਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਠੀਕ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਚੁਣ ਕੇ ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ-
(ਅਰਪਣ, ਮਕਾਨ, ਦਾਨ, ਗੰਨੇ, ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ )
(ੳ) ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਗ਼ਦਰ-ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੇ ਪਹਿਲੇ . ……. ਸਨ |
(ਅ) ਸਾਰੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਮਾਦ ਦੇ ਖੇਤ ਵਿਚ ਜਾ ਕੇ ………….. ਚੂਪਣ ਲ਼ਈ ਕਿਹਾ ।
(ਇ) ਇਹ ਮੱਝ ਸਕੂਲ ਨੂੰ ……. ਦੇਣ ਲਈ ਖੋਲ੍ਹ ਦਿਓ ।
(ਸ) ਮਾਤਾ ਜੀ ਵੀ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਭਲਾਈ ਲਈ ਸਭ ਕੁੱਝ ………….. ਨੂੰ ਲਈ ਤਿਆਰ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
(ਹ) ਮੇਰੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਚੱਜ ਨਾਲ ਰਹਿਣ ਜੋਗੇ ………… ਨਹੀਂ ਜੁੜੇ ।
ਉੱਤਰ:
(ੳ) ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦੇ ਪਹਿਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਧਾਨ ਸਨ ।
(ਅ) ਸਾਰੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਕੰਮਾਦ ਦੇ ਖੇਤ ਵਿਚ ਜਾ ਕੇ ਗੰਨੇ ਚੂਪਣ ਲਈ ਕਿਹਾ ।
(ਇ) ਇਹ ਮੱਝ ਸਕੂਲ ਨੂੰ ਦਾਨ ਦੇਣ ਲਈ ਖੋਲ੍ਹ ਦਿਓ ।
(ਸ) ਮਾਤਾ ਜੀ ਵੀ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਭਲਾਈ ਲਈ ਸਭ ਕੁੱਝ ਅਰਪਣ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਤਿਆਰ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
(ਹ) ਮੇਰੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਜਨਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਚੱਜ ਨਾਲ ਰਹਿਣ ਜੋਗੇ ਮਕਾਨ ਨਹੀਂ ਜੁੜੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਪੜੋ, ਸਮਝੋ ਤੇ ਲਿਖੋ-
ਆਸ਼ਰਮ – ਅਸਥਾਨ, ਰਹਿਣ ਦਾ, ਡੇਰਾ ।
ਮੋਹ –
ਕਮਾਦ –
ਸੰਤਾਨ –
ਸੇਵਾ-ਵਲ –
ਆਮਦਨ –
ਅਰਪਣ –
ਆਲੀਸ਼ਾਨ –
ਹਮਦਰਦ –
ਸਿਹਤਮੰਦ –
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਆਸ਼ਰਮ – ਅਸਥਾਨ, ਰਹਿਣ ਦਾ ਡੇਰਾ ।
ਮੋਹ – ਪਿਆਰ ।
ਕਮਾਦ – ਗੰਨੇ ਦੀ ਫ਼ਸਲ ।
ਸੰਤਾਨ – ਔਲਾਦ, ਬਾਲ-ਬੱਚਾ ।
ਸੇਵਾ-ਫਲ – ਮਿਹਨਤਾਨਾ (ਕੰਮ ਕਰਨ ਬਦਲੇ ਮਿਲੇ ਰੁਪਏ) ।
ਆਮਦਨ – ਕਮਾਈ, ਮੁਨਾਫ਼ਾ ।
ਅਰਪਣ – ਭੇਟਾ, ਦਾਨ ।
ਆਲੀਸ਼ਾਨ – ਸ਼ਾਨਦਾਰ ।
ਹਮਦਰਦ – ਦੁੱਖ ਵੰਡਾਉਣ ਵਾਲਾ ।
ਸਿਹਤਮੰਦ – ਅਰੋਗ, ਰਾਜ਼ੀ ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੀ ਵਾਕਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰੋ-
ਦੇਸ਼-ਭਗਤ, ਕਿਰਤੀ-ਕਿਸਾਨ, ਮੁੱਖ ਅਧਿਆਪਕ, ਸਕੂਲ-ਵੰਡ, ਸਾਂਝੀ-ਵੰਡ, ਸੇਵਾ-ਫਲ, ਅਰਪਣ, ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ !
ਉੱਤਰ:
- ਦੇਸ਼-ਭਗਤ (ਦੇਸ਼ ਨੂੰ ਪਿਆਰ ਕਰਨ ਵਾਲਾ)-ਸ਼ਹੀਦ ਭਗਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਦੇਸ਼-ਭਗਤ ਸੀ ।
- ਕਿਰਤੀ-ਕਿਸਾਨ (ਮਜ਼ਦੂਰਾਂ ਤੇ ਕਿਸਾਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ)-ਕਮਿਊਨਿਸਟ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਵਿਚ ਆਮ ਕਰਕੇ ਕਿਰਤੀ-ਕਿਸਾਨ ਲੋਕ ਸ਼ਾਮਿਲ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਮੁੱਖ ਅਧਿਆਪਕ (ਸਕੂਲ ਦਾ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਅਧਿਆਪਕ)-ਸਾਡੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਅਧਿਆਪਕ ਸਾਹਿਬ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਸ: ਬਖ਼ਸ਼ਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਕੂਲ-ਫੰਡ (ਸਕੂਲ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਆਉਣ ਵਾਲਾ ਪੈਸਾ)-ਮੈਂ ਆਪਣੇ ਪਿੰਡ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਾਇਮਰੀ ਸਕੂਲ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ 3000 ਰੁ: ਸਕੂਲ-ਫੰਡ ਵਜੋਂ ਦਿੱਤੇ ।
- ਸਾਂਝੀ-ਵੰਡ (ਸਾਂਝਾ ਵੰਡਣ ਦਾ ਕੰਮ-ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਸਾਂਝੀ-ਵੰਡ ਕਰਦਿਆਂ ਇੱਕੋ ਆਤੂ ਭੋਰਾ-ਭੋਰਾ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਸਾਰੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਵੰਡ ਦਿੱਤਾ ।
- ਸੇਵਾ-ਫਲ (ਸੇਵਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਬਦਲੇ ਪੈਸੇ ਆਦਿ ਮਿਲਣਾ)-ਮੈਂ ਕਾਲਜ ਵਿਚ ਐੱਨ. ਐੱਸ. ਐੱਸ. ਦੀ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕਰਦਾ ਹਾਂ ਤੇ ਮੈਨੂੰ ਸੇਵਾ-ਫਲ ਵਜੋਂ 600 ਰੁ: ਮਹੀਨਾ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਅਰਪਣ (ਭੇਟ ਕਰਨਾ)-ਕਰਤਾਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਰਾਭੇ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਦਗੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਲਈ ਅਰਪਣ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ ।
- ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ (1913-1914 ਵਿਚ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨ ਦੀ ਅਜ਼ਾਦੀ ਲਈ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਵਿਚ ਬਣੀ ਪਾਰਟੀ)1913-1914 ਵਿਚ ਸ਼ਹੀਦ ਕਰਤਾਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਰਾਭਾ ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਇਨਕਲਾਬੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਭਗਤ ਸੀ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਇਸ ਪਾਠ ਵਿਚ ਆਏ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਜਾਣਦੇ ਹੋ ?
ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ, ਰਾਜਦੂਤ, ਸਿਰਕੀਆਂ ।
ਉੱਤਰ:
- ਗ਼ਦਰ ਪਾਰਟੀ-ਭਾਰਤ ਤੇ ਅਮਰੀਕਾ ਆਦਿ ਮੁਲਕਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਰਹਿਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਹਿੰਦੁਸਤਾਨੀ ਦੇਸ਼ ਭਗਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਇੱਕ ਜਥੇਬੰਦੀ, ਜਿਸ ਦਾ ਪ੍ਰੋਗਰਾਮ . ਅੰਗਰੇਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੱਢਣਾ ਸੀ ।
- ਰਾਜਦੂਤ-ਕਿਸੇ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਵਲੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਹੋਰ ਦੇਸ਼ ਦੀ ਸਰਕਾਰ ਵਲ ਕਿਸੇ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ ਮੰਤਵ ਲਈ ਭੇਜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਸਥਾਈ ਪ੍ਰਤਿਨਿਧ, ਦੁਤ ।
- ਸਿਰਕੀਆਂ-ਕਾਨਿਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਤੀਜ਼ਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾਲਨਾਲ ਜੋੜ ਕੇ ਤੇ ਵਿਚ ਦੀ ਰੱਸੀ ਲੰਘਾ ਕੇ ਬਣਾਇਆ ਤੱਡਾ ਜੋ ਛੱਤ ਪਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਵਰਤਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 12.
ਅਧਿਆਪਕ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਵਾਕ ਬੋਲ ਕੇ ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਲਿਖਾਉਣ
(ਉ) ਸਕੂਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਾਰੇ ਰਲ ਕੇ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਸਨ ।
(ਅ) ਬਾਬਾ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਪਿੰਡ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਕੂਲ ਦੀ ਉਸਾਰੀ ਕਰਵਾਈ ।
(ਇ) ਰਾਜਦੂਤ ਬੜਾ ਹੈਰਾਨ ਹੋਇਆ ।
(ਸ) ਸਕੂਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਿੰਦਗੀ ਬਣਦੀ ਹੈ ।
(ਹ) ਸਾਂਝੀ ਵੰਡ ਤੋਂ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਬਹੁਤ ਖੁਸ਼ੀ ਹੋਈ ।
ਉੱਤਰ:
(ਨੋਟ-ਅਧਿਆਪਕ ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਇਸਦਾ ਅਭਿਆਸ ਕਰਾਉਣ ।)
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਬਾਬਾ ਸੋਹਣ ਸਿੰਘ ਭਕਨਾ ਦੇ ਜੀਵਨ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ ਗੱਲਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਗੋਲ ਚੱਕਰਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਲਿਖੋ :-
ਉੱਤਰ:
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
‘ਠੰਢ (ਸਰਦੀ) ਦਾ ਇਕ ਦਿਨ ਵਿਸ਼ੇ ਉੱਤੇ ਲੇਖ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ:
(ਨੋਟ-ਇਹ ਲੇਖ ਲਿਖਣ ਲਈ ਦੇਖੋ ਅਗਲੇ ਸਫ਼ਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਲੇਖ-ਰਚਨਾ’ ਵਾਲਾ ਭਾਗ ।)