Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Social Science Book Solutions Economics Chapter 2 Human Resources Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 Human Resources
SST Guide for Class 9 PSEB Human Resources Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
India stands __________ in the world as regards to the size of the population.
Answer:
Second
Question 2.
Uneducated people become a __________ for the society rather than an asset.
Answer:
Liability
Question 3.
The size of population of a country along with its efficiency, education qualification, productivity etc. is termed as __________
Answer:
Human resources
Question 4.
In __________ sector production activities are done by using natural resources.
Answer:
Primary
![]()
Question 5.
__________ activities helps in the production of goods and services :
Answer:
Economic.
II. Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Agriculture economy is an example of which sector?
(a) Primary
(b) Tertiary
(c) Secondary.
Answer:
(a) Primary
Question 2.
In agriculture sector there is unemployment for 5 to 7 months. Name this unemployment.
(a) Disguised unemployment
(b) Seasonal unemployment
(c) Educated unemployment.
Answer:
(b) Seasonal unemployment
Question 3.
What is the working age for population in India ?
(a) 15-59 years
(b) 18-58 years
(c) 6-60 years.
Answer:
15 – 59 years
Question 4.
How much is the population of India according to census 2011 ?
(a) 1210.19 million
(b) 130 million
(c) 121.19 million.
Answer:
1210.19 million.
III. True/False :
Question 1.
Working of a housewife in home is an economic activity.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
There is more disguised unemployment in cities.
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 3.
A country develops by investing in human capital.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
The population of a country should be healthy for its economic growth.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
In India literacy rate increased from 1951 to 2011.
Answer:
True
IV. Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question 1.
Name two natural resources.
Answer:
Two natural resources are:
- Air
- Minerals.
Question 2.
How did countries like Germany and Japan make rapid economic development?
Answer:
The countries like Germany and Japan made rapid economic development only due to investment in human resources, specially in th6 field of education and health.
Question 3.
What are economic activities?
Answer:
Economic activities are those activities which are performed to earn money.
Question 4.
What are the two economic activities done by Gurpreet and Mandeep?
Answer:
Gurpreet works in the field and Mandeep gets a job in a private company.
![]()
Question 5.
Give two examples of secondary sector.
Answer:
Two examples of secondary sector are :
- Manufacturing of jaggery from sugarcane.
- Manufacturing of cotton cloth from raw cotton.
Question 6.
What are non-economic activities ?
Answer:
Non-economic activities are those activities which do not give income in return.
Question 7.
Give two determinants of the quality of population.
Answer:
- Good education
- Health of people.
Question 8.
Name the state with the highest literacy rate.
Answer:
Kerala.
Question 9.
Name the step taken to provide elementary education to all children in the age group of 6 – 14 years.
Answer:
Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the age limit of the work force population in India?
Answer:
15 – 59 years.
Question 11.
Name two programmes undertaken by the government of India to generate employment opportunities.
Answer:
- Swaran Jayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana (SJGSY)
- Sampoorna Gramin Rozgar Yojana (SGRY).
V. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by human resources?
Answer:
The size of the population of a country along with its efficiency, educational qualities, productivity, etc. is known as human resources. Human resource is the most important resource because it makes the natural resources more useful. A country with highly educated and trained people can efficiently increase its productivity.
Question 2.
How human resources is superior to other resources like land and physical capital?
Answer:
Human capital is superior to other resources like land and physical capital which are not useful at their own. Human resources can make use of land and capital. So, a large population is not a liability. It can be turned into a productive asset by investment in human capital. For example, by spending on education and health for all, training of industrial and agriculture workers in the use of modern technology etc. development of a country can be increased.
Question 3.
What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
Answer:
|
Economic Activities |
Non-Economic Activities |
| 1. All those activities which are performed to earn money are called economic activities. | 1. All those activities which do not give income in return are non economic activities. |
| 2. Economic activities add value to the national income. | 2. Non economic activities do not add value to the national income. |
| 3. Economic activities contribute to the flow of goods and services in an economy | 3. They do not contribute to the flow of goods and services in the economy. |
| 4. Examples. Mandeep doing a job in a private company, teacher teaching in a school | 4. Examples. Housewives stitch their own suits, teacher teaches his son at home. |
![]()
Question 4.
What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Answer:
Education is an important input for the growth of human capital. It provides new aspirations and develops values of life. Education contributes towards the growth of not only of a single person but also towards the growth of society as a whole. We get an opportunity to study in a school which helps us to become a good citizen and enables to earn a good salary in the future which in turn increases the national income and hence helps the economy to develop. Thus education plays a vital role in human capital formation.
Question 5.
What are the steps taken by the Government of India to spread education?
Answer:
The following steps are taken by the Government of India to spread education :
- Number of educational institutions have been established.
- The Primary school system has expanded to over more than 5,00,000 villages in India.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’ has been launched to provide compulsory elementary education to all children in the age group of 6-14 years.
- Mid-day meal scheme has been implemented to improve the nutritional status of the children.
- Navodaya Vidyalayas are being established in each district.
- Vocational streams have been introduced to impart training to students for self-employment.
Question 6.
Explain the term unemployment. Which groups of people are not included while determining a country’s unemployment rate?
Answer:
The term unemployment refers to a situation in which people are willing to work at the current wages but cannot find work. The work force population includes people from 15 years to 59 years. Person beyond this age limit, people looking after the household chores, children, old people are not to be called unemployed as they all contribute to the flow of goods and services.
Whenever a country’s unemployment is determined, persons who are not able to work, for example, patients, old people, small children, students etc. are not included.
Question 7.
Give two reasons for unemployment in India.
Answer:
- The rapidly increasing number of schools and colleges tend to increase unemployment as the job opportunities have not increased in the same rate.
- Rapidly increasing population leads to unemployment in the country. In the rural areas there is seasonal and disguised unemployment. Urban areas have educated unemployment.
Question 8.
Distinguish between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment.
Answer:
Disguised unemployment means more people are engaged in a particular work than required. Even if some men are relieved from work the total productivity will not decline. In India, 30 percent of the total working rural population is disguised unemployed.
Seasonal unemployment means when people find jobs during some months and during remaining months they are unemployed. In the agriculture sector people remain unemployed for nearly 5, to 7 months.
Question 9.
Why is educated unemployment rapidly increasing in urban areas?
Answer:
Unemployment is more in urban areas as compared to rural areas. In case of urban areas the rapidly increasing number of schools and colleges lead to educated unemployment as the job opportunities have not increased in the same rate.
![]()
Question 10.
How does literate and ill health affect the growth of the economy?
Answer:
The quality of population decides the growth rate of the economy. Literate population is an asset to the economy and ill health is a liability for the economy. Literate persons are important input for the grow of the economy. It provides new aspirations and develops values of life. Literate person contributes towards the growth of not only of a single person but also towards the growth of society as a whole. On the other hand ill health is a condition in which a person is not mentally and physically fit.
VI. Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Visit your village or your colony and find out:
(i) Whether the women in different houses work at home or go outside to work?
Answer:
In my village some of the women work at home and others go outside to work. They go to work in the fields, offices and for cleaning other’s house.
(ii) Their work is an economic or non economic activity?
Answer:
The women who are doing household chores are doing non-economic activities. On the other hand who work in the fields, offices and cleaning other’s house are doing economic activities.
(iii) Give two examples each of economic activity and non-economic activity.
Answer:
Economic activities,
(a) Raj doing a job in a multinational company
(b) Doctor serving the patients in a hospital.
Non-Economic activities,
(a) Domestic work done by housewife
(b) A teacher teaching his son at home.
(iv) Work done by your mother is an economic or non-economic activity.
Answer:
My mother is a teacher in a government school. So she is doing economic activity.
Question 2.
Literacy rates in India
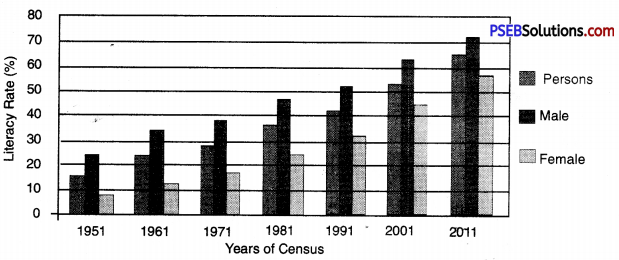
Study the graph and answer the following questions :
(i) Has literacy rate increased between year 1951 to year 2011?
Answer:
Yes, the literacy rate has increased between year 1951 to year 2011 as it is evident from the bar diagram.
(ii) In which year India crossed the literacy rate of 50%?
Answer:
In the year 2001, India crossed the literacy rate of 50%.
(iii) In which year India has the highest literacy rate?
Answer:
In the year 2011, India has the highest literacy rate.
(iv) In which year the literacy rate among the women is the highest?
Answer:
The literacy rate among the woman is the highest in the year 2011.
(v) Why literacy rate is low among the women as compared to the men of India? Discuss with your teacher.
Answer:
The literacy rate is low among the women as compared to men of India because people send their girl child in less number as compared to boy. They engage girls in household chores.
![]()
Question 3.
Table Health Services in India
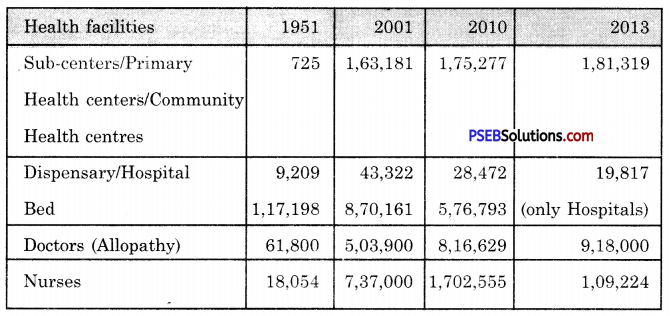
Source: National Health Profile, 2010 D/O Ayush, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. National Health Profile, 2013.
Let’s Discuss
Read the table and answer the following questions :
(i) Number of dispensaries and hospitals increased in 1951-2010.
Answer:
It is clear from the table that the number of dispensaries and hospitals did not increase in 1951-2010.
(ii) Number of doctors increased in 2001-2013.
Answer:
Yes, the number of doctors increased in 2001-2016.
(iii) Number of beds qued in health institution 1951-2013.
Answer:
Yes, the number of beds qued in health institution increased in 1981-2016.
(iv) Visit your village or a nearby village dispensary and find out which facilities are provided and which are needed more.
Answer:
By visiting my village dispensary, it is found that there is a shortage of staff. Even doctor has not joined the dispensary. Only one pharmasist was looking after the dispensary. Other facilities were in good condition.
PSEB 9th Class Social Science Guide Human Resources Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Population can be for the economy.
(a) Asset
(b) Liability
(c) Both asset and ability
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both asset and ability
Question 2.
In which field, the investment formulates human capital?
(a) Education
(b) Health
(c) Training
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 3.
Which does indicate the human capital formation in India?
(a) Green Revolution
(b) I.T. Revolution
(c) Labour Revolution
(d) White Revolution.
Answer:
(b) I.T. Revolution.
Question 4.
Cooking the food, cleaning the clothes and utensils by Sheela is what kind of activity?
(a) Economic activity
(b) Non-economic activity
(c) Wealth activity
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Non-economic activity.
![]()
Question 5.
Agriculture, forestry and dairy come under which sector?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Primary
Question 6.
Construction and manufacturing comes under sector.
(a) Secondary
(b) Tertiary
(c) Primary
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(a) Secondary.
Question 7.
Trade, transport, communication and banking etc. come under which sector?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Tertiary.
Question 8.
What is the life expectancy at birth in India?
(a) 66 years
(b) 70 years
(c) 55 years
(d) 15.8 years.
Answer:
(d) 15.8 years.
Question 9.
What is the crude birth rate per thousand in India?
(a) 26.1
(b) 28.2
(c) 20.4
(d) 35.1.
Answer:
(a) 26
Question 10.
What is the death rate per thousand in India?
(a) 9.8
(b) 8.7
(c) 11.9
(d) 25.1.
Answer:
(b) 8.7.
![]()
Question 11.
What was the literacy rate of India in 2001?
(a) 65%
(b) 75%
(c) 60%
(d) 63%.
Answer:
(a) 65%.
Question 12.
What type of unemployment exists in rural areas of India?
(a) Seasonal
(b) Disguised
(c) Both seasonal and disguised
(d) Voluntary.
Answer:
(c) Both seasonal and disguised.
Question 13.
What type of unemployment mainly remains in the urban areas?
(a) Seasonal
(b) Voluntary
(c) Disguised
(d) Educated.
Answer:
(d) Educated.
Question 14.
Shifting of labours from rural area to urban area in search of work is known as
(a) Migration
(b) Immigration
(c) Invention
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Migration
Question 15.
In which Held, the investment increases the production capacity of country?
(a) Land
(b) Physical capital
(c) Human capital
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 16.
Which one is the example of primary sector?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Manufacturing
(c) Communication
(d) Trade.
Answer:
(a) Agriculture.
![]()
Question 17.
Which one is the example of secondary sector?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Manufacturing
(c) Communication
(d) Banking.
Answer:
(b) Manufacturing.
Question 18.
Which one is the example of tertiary sector?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Manufacturing
(c) Banking
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Banking
Question 19.
In which year, India achieved the highest literacy rate?
(a) 2001
(b) 1991
(c) 2000
(d) 1981.
Answer:
(a) 2001.
Question 20.
What kind of people are the liability for the economy?
(a) Educated
(b) Healthy
(c) Unhealthy
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Unhealthy.
Question 21.
When was the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan launched in India?
(a) 2008
(b) 2010
(c) 2007
(d) 2005.
Answer:
(b) 2010.
Question 22.
Which is not associated with primary sector?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Forestry
(c) Education
(d) Mining.
Answer:
(c) Education.
Question 23.
Which of the following is not an activity of tertiary sector?
(a) Transport
(b) Banking
(c) Manufacturing
(d) Tourism.
Answer:
(c) Manufacturing.
Fill in the Blanks:
Question 1.
China stands __________ in the world as regards to the size of the population.
Answer:
First
Question 2.
Ill health people become a __________ for the society rather than an asset.
Answer:
Liability
![]()
Question 3.
Japan made investment in __________ resources.
Answer:
Human
Question 4.
Domestic work done by housewife __________ is activity.
Answer:
Non-economic
Question 5.
__________ had the lowest literacy rate in India in 2011.
Answer:
Bihar
Question 6.
According to census 2011 total literacy rate in India is __________ per cent.
Answer:
74.
True/False:
Question 1.
Literate and healthy population are liability.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
According to 2011 census. Literacy among men is 82.10 percent.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Average unemployment rate of India during the period of 1983 to 2011 remained at 9 percent.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Quality of population does not depend upon good health and education.
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 5.
Mining and forestry are the activities of secondary sector.
Answer:
False.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In which fields, does investment formulate human capital?
Answer:
In fields such as education, health, training etc. the investment formulates human capital.
Question 2.
What is unemployment?
Answer:
Unemployment is a situation under which people are willing to work at the prevailing wages but are unable in find any work.
Question 3.
What type of unemployment exists in rural areas of India?
Answer:
In rural areas of India, both seasonal and disguised unemployment exist. Question 4. Which is the most labour absorbing sector of the Indian economy? Answer:Agriculture is the most labour absorbing sector of the Indian economy.
Question 5.
What is seasonal unemployment?
Answer:
When people work for a few months but are not able to find jobs during the remaining months of the year, it is called as seasonal unemployment.
Question 6.
What do you understand by ‘people as resources’?
Answer:
‘People as Resources’ is a way of referring to a country’s working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities.
![]()
Question 7.
What are market activities?
Answer:
Market activities involve remuneration to anyone who works, i.e., activities performed for pay or profit are called market activities.
Question 8.
What do you understand by the concept of Non-marketing activities?
Or
What are non-marketing activities?
Answer:
Non-marketing activities are those activities which do not involve remuneration to anyone who performs. These activities are performed for self¬consumption and are not for sale.
Question 9.
What are the two major determinants of earning?
Answer:
Two major determinants of earning for any individual are education and skill.
Question 10.
Which type of unemployment mainly exists in urban areas of India?
Answer:
Educated unemployment mainly exists in the urban areas of India.
Question 11.
Define the concept of migration.
Answer:
The concept of migration refers to the movement of people from one region to another in search of work or for better future prospects.
Question 12.
What are the various types of economic activities? Name them.
Answer:
There are two types of economic activities. These are :
- Marketing activities
- Non-marketing activities.
![]()
Question 13.
What is National Income?
Answer:
It is a sum of total goods and services produced in a country within a year.
Question 14.
What do you know about Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan?
Answer:
It is a scheme under which elementary education is to be provided to all children in the age group of 6 to 14 years.
Question 15.
Write any two types of urban unemployment.
Answer:
Two types of urban unemployment are :
- Educated unemployment
- Industrial unemployment.
Question 16.
What kind of people are a liability for the economy?
Answer:
Illiterate and unhealthy people are a liability for the economy.
Question 17.
Define the concept of’Birth Rate’.
Answer:
The Birth Rate refers to the number of live births for every 1000 population during a particular period of time.
Question 18.
What is ‘Death Rate’?
Answer:
The Death rate refers to the number of deaths per thousand population, during a particular period of time.
![]()
Question 19.
Cooking food, cleaning clothes and utensils by Sheela in her home is what kind of activity?
Answer:
It is a non-economic activity.
Question 20.
Trade, transport, communication and banking, etc., belong to which sector?
Answer:
They belong to the Tertiary sector.
Question 21.
What does CHC stand for?
Answer:
CHC stands for Community Health Centre.
Question 22.
What is the full form of GNP?
Answer:
The full form of GNP is Gross National Prodilct.
Question 23.
What does the acronym PHC stand for?
Answer:
The acronym PHC stands for Primary Health Centre.
Question 24.
Which sector is also known as the service sector?
Answer:
Tertiary sector is also known as the service sector.
Question 25.
Which state has the highest percentage of literacy in India?
Answer:
Kerala has the highest percentage of literacy in India.
Question 26.
What is the life expectancy rate of India?
Answer:
Life expectancy rate of India was 67.80 years in 2011.
Question 27.
What was death rate and birth rate of India in 2011?
Answer:
In 2011, death rate was 7.2 and birth rate was 22 per thousand in India.
Question 28.
What are the activities included in a primary sector?
Answer:
The primary sector includes agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishing, poultry farming and mining.
Question 29.
Which factors are responsible for non-market activities?
Answer:
Factors such on processing of primary products, subsistence farming, etc., are responsible for non-market activities.
![]()
Question 30.
State one example of tertiary sector.
Answer:
Banking.
Question 31.
What was the literacy rate of India in 2011?
Answer:
The literacy rate of India was 74.04% in 2011.
Question 32.
On what factors does the quality of population depend?
Answer:
The quality of population depends upon the literacy level, health of an individual in terms of life expectancy and skills developed by the people of a country.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the quality of population.
Answer:
The quality of population depends upon the health of a person, life expectancy, skill formation acquired and the literacy rate. The quality of population decides the growth rate of the country. Literate and healthy people are an asset for the economy. On the other hand, illiterate and unhealthy people are a liability.
Question 2.
Explain in brief the importance of education.
Answer:
Education is important due to the following reasons :
- Education is an important input for the growth of everyone.
- It provides new aspiration and develops values of life.
- It enhances the national income, cultural richness of the country.
- It increases the efficiency of governance.
- It helps in getting good job and salary.
Question 3.
Define unempolyment. What are its consequences?
Answer:
Unemployment is said to exist when people who are willing to work at the existing wages cannot find jobs.
Following are the consequences of unemployment.
- It leads to wastage of manpower resource.
- It leads to increased overlead. As a result the dependence of unemployed on the working populatison increases.
- Increase in unemployment is an indicator of a depressed economy.
- It increases many social evils among the young generation.
Question 4.
What is meant by disguised unemployment?
Answer:
In case of disguised unemployment people appear to be employed. They have agricultural plot where they find work. This usually happens among family members engaged in agricultural activity. The work requires the service of five people but engages eight people. If three people are removed, the productivity of the field will not decline. The field requires the service of five people and the three extra people are disguisedly unemployed.
Question 5.
What is meant by seasonal unemployment?
Answer:
Seasonal unemployment happens when people are not able to find jobs during some months of the year. People dependent upon agriculture usually face such kind of problem. There are certain busy seasons when sowing, harvesting, weeding, threshing is done. Certain months do not provide much work to the people dependent on agriculture.
Question 6.
What is meant by educated unemployment?
Answer:
In case of urban areas educated, unemployment has become a common phenomenon. Many youth with matriculation, graduation and post graduation degrees are not able to find job. A paradisiacal manpower situation is witnessed as surplus of manpower in certain categories exsists with shortage of manpower in others.
![]()
Question 7.
State the meaning of market and non-market activities.
Answer:
Market activities involve remuneration to any one who performs i.e. activity performed for pay or profit. These include production of goods and services while the non-market activities are the production for self-consumption. There can be consumption and processing of primary product and own account production of fixed capital.
Question 8.
Define population as a human resource.
Answer:
This is the positive side of a large population that is often overlooked when we look only at the negative side, considering only the problems of providing the population with food, education and access to health facilities. When the existing ‘human resource’ is further developed by becoming more educated and healthy, we call it ‘Human Capital Formation’.
Question 9.
What are the various activities undertaken in the secondary and tertiary sectors?
Answer:
In the secondary sector, the quarrying and manufacturing activities are done. In the tertiary sector trade, transport, communication, banking, education, health, insurance, etc. activities are done.
Question 10.
State the role of health in human capital formation.
Answer:
Health plays a very important role in human capital formation. The health of a person helps him to realise his potential and the ability to fight illness. An unhealthy person becomes a liability for an organisation. Health is an indispensable basis for realising one’s well being.
Question 11.
What are economic activities? Explain.
Answer:
Economic activities are those activities that contribute to the flow of goods and services in the economy. These activities add value to the national income.
Economic activities have two parts
- Market activities and
- Non-market activities.
1. Market activities. It involves remuneration .to anyone who performs i.e., activity performed for pay or profit.
2. Non-market activities. Non-market activities are the production of goods for self-consumption. There can be consumption and processing of primary products and own account production of fixed assets.
Question 12.
Distinguish between market and non-market activities.
Answer:
Following are the main differences between market and non-market activities.
|
Market Activities |
Non-market Activities |
| 1. Market activities involve remuneration to any one who performs i.e., activity performed for pay or profit. | 1. None market activities are the production of self consumption. |
| 2. These include production of goods or services including government service. | 2. These can be consumption, processing of primary product and own account .production of fixed assets. |
| 3. A worker working in a mine, teacher teaching in a school etc. are some examples of market activities. | 3. Processing of primary products, subsistence farming, etc. are non market activities. |
![]()
Question 13.
(i) What is Gross National Product?
Answer:
Gross national product is the money value of all goods and services produced by the residents of the country. It includes all final goods and services produced by the residents of the country anywhere in the world.
(ii) Countries like Japan did not have any natural resources, still they are developed countries. Give reasons.
Answer:
(a) Japan has invested on human capital especially in the field of education and health.
(b) The skilled and trained people have made efficient use of other resources like land and capital.
(c) Efficiency and technology evolved by people have made these countries developed.
Question 14.
(i) Name any two types of unemployment which prevail in rural areas.
Answer:
(a) Disguised unemployment and
(b) Seasonal unemployment mostly prevails in the rural areas
(ii) Mention any four factors on which the quality of population depends.
Answer:
(a) Health
(b) Life expectancy
(c) Education
(d) Skill
(iii) Which sector (in the primary sector) is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy?
Answer:
Agriculture sector is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy.
Question 15.
(i) Mention any two activities which are included in the primary sector.
Answer:
(a) Fishing
(b) Mining
(ii) Mention any two activities which are included in the service sector.
Answer:
(a) Banking
(b) Insurance
(iii) Mention any two activities which are included in the secondary sector.
Answer:
(a) Quarrying
(b) Manufacturing.
Question 16.
(i) Name any four factors which can improve the quality of human resources.
Answer:
(a) Education
(b) Health
(c) Technology
(d) Training.
(ii) Name any four factors of production.
Answer:
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Capital
(d) Entreprenuer.
![]()
Question 17.
What is ‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’?
Answer:
‘Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan’, is a step towards providing elementary education to all children in the age group of 6 – 14 by 2010. It is a time bound initiative of the central government in partnership with the states, the local government and the community for achieving the goal of universalisation of elementary education.
Question 18.
(i) What types of unemployment are found in agriculture?
Answer:
Disguised and seasonal unemployment are found in agriculture.
(ii) State the meaning of disguised unemployment.
Answer:
Disguised unemployment is that type of unemployment under which people appear to be employed but they are not.
Question 19.
‘Improvement in the health status of the population has been the priority of a country.’ Give reasons.
Answer:
- Good health increases the efficiency of the worker.
- An unhealthy worker becomes a liability for the country.
- Healthy citizens are the basic factors of production.
- The health of a person helps him to realise the potential and the ability to fight illness.
Question 20.
‘Investment in human capital yields a return just like investment in physical capital.’ Explain.
Answer:
- Human capital increases the productivity of the workers.
- Human capital adds to the quality of labour.
- Educated, trained and healthier people can use natural resources in a better way.
- A country can earn foreign exchange by exporting services of human resources.
Question 21.
Group the following activities into primary, secondary and tertiary activities.
Banking, insurance, dairy, quarrying, mining, communication, education, fishing, poultry farming, agriculture, manufacturing, forestry, tourism and trade.
Answer:
|
Primary |
Secondary |
Tertiary |
| 1. Dairy | 1. Quarrying | 1. Banking |
| 2. Mining | 2. Manufacturing | 2. Insurance |
| 3. Fishing | 3. Communication | |
| 4. Poultry Farming | 4. Education | |
| 5. Agriculture | 5. Tourism | |
| 6. Forestry | 6. Trade |
Question 22.
What are the objectives of the Tenth Five Year Plan with reference to education?
Answer:
Following are the main objectives of the Tenth Five Year Plan with reference to education.
- The Tenth Five Year Plan endeavoured to increase the enrolment in higher education of the 18 – 23 year age group from the present 6-9 percent, by the end of the plan period.
- The Tenth Five Year Plan also focuses on distant education, convergence of formal, non-formal, distant and IT education institutions.
- The strategy focus on increasing access, quality, adoption of states-specific curriculum modification, vocationalisation and networking on the use of information technology.
Question 23.
Define unemployment. What are the major types of unemployment prevailing in India?
Answer:
Unemployment is a situation in which a person is willing to work at the prevailing wages, but does not find any gainful work.
- Seasonal unemployment
- Educated unemployment
- Disguised unemployment
- Structural unemployment
- Technical unemployment.
Question 24.
What are the two types of unemployment which are prevailing in rural areas? Write any four factors responsible for this.
Answer:
- Seasonal unemployment and
- Disguised unemployment are prevailing in rural areas.
Causes :
- Lack of diversification of agriculture.
- Lack of capital.
- Large families due to overpopulation.
- Underdevelopment of cottage and small scale industries.
Question 25.
Distinguish between disguised unemployment and educated unemployment.
Answer:
Following are the main differences between disguised and educated unemployment :
|
Disguised Unemployment |
Educated Unemployment |
| 1. Disguised unemployment is that type of unemployment under which people appear to be employed, but they are not. | 1. Educated unemployment is that type of unemployment under which people are educated but are unable to find a job. |
| 2. It is mainly found in rural areas. | 2. It is mainly found in urban areas. |
Question 26.
Explain the employment scenario in the three sectors.
Answer:
- Primary sector. In India, agriculture is the most labour absorbing sector of the economy. But it is facing disguised unemployment. It does not have any capacity to absorb more workers. So surplus workers are moving to the secondary and the tertiary sectors.
- Secondary sector. In secondary sector, small scale manufacturing is also labour absorbing Industry. Cottage industry should also be set up in rural areas.
- Tertiary sector. Tertiary sector is the most important sector which can help in removing the unemployment problem.
Question 27.
What is seasonal unemployment? What are the factor responsible for this unemployment?
Answer:
Seasonal unemployment is that type of unemployment in which a worker is employed during some parts of the year and remains without work during the rest of the year.
Causes
- Lack of multiple cropping.
- Lack of small scale and cottage industries in rural areas.
- Lack of commercialisation of agriculture.
Question 28.
What is disguised unemployment? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer:
Disguised unemployment is a situation in which more workers are working in an activity than required. The people, who are actually engaged in such an activity appear to be employed, but are not fully employed. For example, if for the cultivation of one hectare land 12 workers are required, but instead of 12 workers, 20 workers are working. In this case, 8 workers are disguised unemployed. In such cases, even if the surplus workers are removed the production does not suffer.
![]()
Question 29.
Why is human capital the most important factor of production? Give three reasons.
Answer:
Human capital is the most important factor of production because:
- Some production activities need literate people.
- Some production activities need physical labour.
- Human capital has only entrepreneurial ability.
Question 30.
How have countries like Japan become rich and developed? Explain three reasons.
Answer:
- They have invested in human capital especially in the field of education and health.
- They have efficiently used the other resources like land and physical capital.
- They have developed the technology and efficiency.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the main problems of human capital formation in India?
Answer:
The following are the problems of human capital formation in India :
1. High cost of Human Capital Formation. In India the cost of human capital formation is very high. Due to high pressure of population, government is investing more in human capital but the returns are very low. Government is opening a large number of educational institutions. In this process high cost of human capital formation is creating problems.
2. Low Level of Adult Education and Agricultural Education. Another problem of human capital formation in India is the low level of adult and agricultural education. Adult education is helpful in changing the attitudes of people. There are only few programmes related to agricultural education. These problems resulted in low productivity.
3. Less Priority to Secondary Education. Government gives less priority to secondary education than primary education and the expenditure on primary education is also high which is unproductive. One can get efficiency in technical knowledge after secondary education. This attitude creates problems in human capital formation.
4. Total Stock of Human Capital Formation. India is a developing country, as a result, there remains great demand of human capital formation in every field. But the total stock of human capital formation is less, due to less resources which creates problems in the country.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the role of human capital formation in economic development.
Answer:
Role of Human Capital Formation in Economic Development:
Economic backwardness is the main feature of underdeveloped countries and the main cause for this backwardness is the problem of human capital formation. But the economic development can be achieved by human capital formation.
There are the following advantages of human capital formation in economic development :
1. Increase in the Efficiency of Labour. Economic development can be attained through an increase in the efficiency of labour. The efficiency of labour is increased through human capital formation by investing in education, health, training, etc.
2. Training and Technical Knowledge. It is necessary for the labour to be trained and educated for economic development. Thus through human capital formation, the level of education, technical knowledge, efficiency, and health of the labour can be raised, and hence the path of economic development can be achieved.
3. To Enlarge the size of the Business. The size of a business can be enlarged by efficient entrepreneurs and innovators. An entrepreneur becomes efficient by investment in human capital and this efficiency ultimately leads to economic development.
4. Increase in Production. An increase in production leads to economic development. Human capital formation produces able and efficient persons who increase production.
5. Change in the Religious, Social, Cultural, and Institutional setup. For economic development change in religious, social, cultural, and institutional setup is necessary. These changes are only possible through human capital formation.
6. To Decrease Production Cost. Reduction in the production cost is essential for economic development. Human capital formation helps to decrease the production cost.
Thus the role of human capital formation in economic development is very significant.