Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Biomolecules Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 9 Biomolecules
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Write the name of any one amino acid, sugar, nucleotide and fatty acid. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Alanine is an amino acid, glucose is a sugar, adenylic acid is a nucleotide and linolenic acid is a fatty acid.
Question 2.
Mention four essential major elements of life.
Answer:
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen are the four essential elements of life.
Question 3.
Name one element invariably found in proteins but not in all carbohydrates and lipids.
Answer:
Nitrogen is found invariably in proteins, but not in all carbohydrates and lipids.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the name given to a polysaccharide composed of two different monomers? Also give example for this.
Answer:
The name given is heteropolysaccharide to the type of polysaccharide, which is composed of different types of monomers, e.g., Pectin.
Question 5.
One of the homopolysaccharide is also known as animal starch. Name it.
Answer:
Glycogen is also known as animal starch.
Question 6.
The macromolecules that forms the hereditary determinants of the living organism. Name it.
Answer:
Nucleic acid.
Question 7.
A nitrogenous base is present in RNA but absent in DNA. Name it. Also give example in which it exists.
Answer:
Uracil (U), is the nitrogenous base present only in RNA, e.g., viruses like hepatitis C.
Question 8.
How many hydrogen bonds are formed between:
(i) Guanine and cytosine
(ii) Adenine and thymine, respectively?
Answer:
(i) Three hydrogen bonds between guanine and cytosine.
(ii) Two hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine.
![]()
Question 9.
Reaction given below is catalysed by oxidoreductase between two substrates A and A, complete the reaction. [NCERT Exemplar] A reduced + A oxidised →
Answer:
A reduced + A’ oxidised → A oxidised + A’ reduced + A’ reduced
Question 10.
Name two physical factors which can affect the enzyme activity?
Answer:
Temperature and pH are the two physical factors that affects activity of an enzyme.
Question 11.
The enzyme that works only in the presence of a co-factor or coenzyme called
Answer:
Apoenzyme works only in the presence of a co-factor or coenzyme.
Question 12.
What do you mean by living state?
Answer:
The living state is a non-equilibrium steady-state to be able to perform work.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Give a tabular representation of different constituents of a living cell.
Answer:
| Component | % of Total Cellular Mass |
| Water | 70-90% |
| Proteins | 10-15% |
| Carbohydrates | 3% |
| Lipids | 2% |
| Nucleic Acids | 5-7% |
| Ions | 1% |
![]()
Question 2.
What are polysachharides?
Answer:
Polysaccharides are long chains of sugars. They are threads containing different monosaccharides as building blocks.
In a polysaccharide chain (say glycogen), the right end is called the reducing end and the left end is called the non-reducing end. Starch forms helical secondary structures. In fact, starch can hold 12 molecules in the helical portion.
Examples: Cellulose, chitin
Question 3.
Give a brief description of nucleic acid.
Answer:
For nucleic acids, the building block is a nucleotide. A nucleotide has three chemically distinct components. One is a heterocyclic compound, the second is a monosaccharide and the third is a phosphoric acid or phosphate.
The heterocyclic compounds in nucleic acids are the nitrogenous bases named adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine. Adenine and Guanine are substituted purines while the rest are substituted pyrimidines. The skeletal heterocyclic ring is called as purine and pyrimidine respectively. The sugar found in polynucleotides is either ribose (a monosaccharide pentose) or 2’ deoxyribose. A nucleic acid containing deoxyribose is called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) while that which contains ribose is called ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Question 4.
What is the difference between primary and secondary metabolites?
Answer:
Primary metabolites are found in both, animal cells and plant cells. Secondary metabolites are found only in plant cells.
Functions of primary metabolites are known to scientists, while functions of secondary metabolites are not known yet.
Question 5.
Explain the basic structure of an amino acid.
Answer:
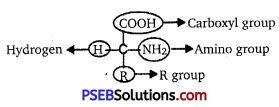
Amino acid is an organic compound, which has an amino group and an acidic group, present
as substituents on the same carbon ; i.e., the a-carbon. Because of this amino acids are also called α-amino acids. On four valency positions there are four substituent groups. They are hydrogen, carboxyl group, amino group and a variable group. The variable group is called the ‘R’ group. The nature of R group decides the type of an amino acid.
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the classification and nomenclature of enzymes.
Answer:
Classification and Nomenclature of Enzymes: The International Union of Biochemists (IUB) has classified all the enzymes into the following six classes:
(a) Class 1: Oxidoreductases: These enzymes catalyse the oxidation (by adding oxygen or removal of hydrogen or removal of electrons) or reduction (by adding hydrogen or adding electrons to a substrate) of a substance.
S reduced + S’ oxidised → S oxidised + S’ reduced
(b) Class 2: Transferases: These enzymes catalyse the transfer of specific groups from one substrate to another. S – G + S’ → S + S’ – G.
(c) Class 3: Hydrolases: These enzymes catalyse the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller molecules with the addition of water.
(d) Class 4: Lyases: These enzymes catalyse the cleavage of specific covalent bonds and removal of specific group (s), without the use of water.
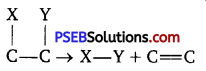
(e) Class 5: Isomerases: These enzymes catalyse the rearrangement of atoms in a molecule to form isomers.
(f) Class 6: Ligases: These enzymes catalyse covalent bonding (of C-0, C-S, C-N, P-O etc.) between two substrates to form a large molecule, mostly involving utilisation of energy by hydrolysis of ATP.
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
Enumerate the difference between a nucleotide and nucleoside. Give two examples of each with their structure. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Differences between nucleotide and nucleoside are given below:
| Nucleotide | Nucleoside |
A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups, i. e., sugar + base + phosphate.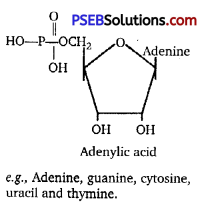 |
A nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base t covalently attached to a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), but without the phosphate group, i. e., sugar + base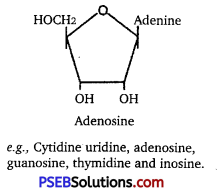 |
Question 2.
What is the concept of metabolism? What are the metabolic basis for living?
Answer:
The continuous process of breakdown and synthesis of biomolecules through chemical reactions occurring in the living cells is called metabolism.
- Each of the metabolic reaction results in a transformation of biomolecules.
- Most of these metabolic reactions do not occur in isolation but are always linked with some other reactions.
- In these reactions, the metabolites are converted into another metabolite in a series of linked reactions called metabolic pathways.
- Each metabolite has a definite rate and direction during the flow through a metabolic pathways called the dynamic state.
In living systems, metabolism involves two following types of pathways:
(a) The anabolic pathway is called biosynthetic pathway. It leads to a more complex structure from a simpler structure, e.g., The pathway involving the conversion of acetic acid into cholesterol. These pathways consume energy.
(b) The catabolic pathways lead to simpler structure from a complex structure, e g., The pathway involving conversion of glucose into lactic acid in our skeletal muscles. This pathway lead to the release of energy, e.g., Energy is liberated when glucose is degraded to lactic acid in our skeletal muscles.
![]()
Question 3.
Formation of Enzyme-Substrate complex (ES) is the first step in catalysed reactions. Describe the other steps till the formation of product.
Answer:
Mechanism of Enzymatic Action: The catalytic cycle of an enzyme action can he described in the following steps :
- First, the substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, fitting into the active site.
- The binding of the substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape, fitting more tightly around the substrate. The formation of the ES complex is essential for catalysis.
E + S → ES → EP → E + P - The active site of the enzyme, now in close proximity of the substrate breaks the chemical bonds of the substrate and the new enzyme product complex is formed.
- The enzyme releases the products of the reaction and the free enzyme is ready to bind to another molecule of the substrate and run through the catalytic cycle one again.