PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Physical Education Chapter 4 Sport Injuries
Physical Education Guide for Class 12 PSEB Sport Injuries Textbook Questions and Answers
One Mark Question-Answers
Question 1.
What are sports injuries?
Answer:
A sports injury may be defined as “damage to the tissues of the body that occurs as a result of sport or exercise” due to overuse, twisting and strectching.
Question 2.
Write any two symptoms of sprain.
Answer:
- Burning, pain, and swelling.
- Severe pain during movement.
![]()
Question 3.
Who participates in sports besides players or sports persons?
Answer:
The persons with active lifestyle and performing regular exercises takes part in sports.
Two Marks Question-Answers
Question 4.
What is compound fracture?
Answer:
It is one in which the skin or mucous membrane wound extends to the fractured bone.
Question 5.
What is green stick fracture?
Answer:
A fracture in which only one side may get broken and the bone then appears to be bent, but not broken. It is most common in children.
Question 6.
What are indirect injuries?
Answer:
The injury does not result from physical contact with an object or person but it caused due to internal force built up the action of the performer such as overstretching and poor technique.
![]()
Three Marks Question-Answers
Question 7.
What is strain? What are the symptoms of strain?
Answer:
Strain is a disruption of the fibres of a muscle or tendon. Tears or strains occur when a muscle or tendon is over-stretched or when a muscle contracts too quickly. The causes of strain occur while lifting weights, muscles are stretched during sudden jerky motion, landing badly on an ankle or walking or exercising on uneven surface. This type of injury generally causes sprains in knees or ankles.
Symptoms:
- Sudden pain at the site of injury.
- Fitness and cramps.
- Swelling at the site of the injuries and sometimes redness also appears.
- Tenderness.
- No movement and numbness.
![]()
Question 8.
Write the treatment of the following:
Answer:
(i) Sprain:
There are few steps for prevention of sprains:
- Sprain is firstly treated as ‘PRICE’, where ‘P’ stands for ‘protection’ and ‘R’ stands for ‘Rest’, ‘I’ stands for ‘Ice application’, ‘C’ stands for ‘Compression’ and E stands for ‘Elevation’. Rest the sprained area. If necessary, use sling for an arm injury or crutches for a leg or foot injury. Apply ice on an injured part for 20 minutes every hour. Never put ice directly against skin or it may damage the skin.
- Give comfortable position to the patient.
- Provide support to the injured part.
- Immobilize and elevate the injured part.
- Cold compression is given to reduce swelling.
- Hot formation is applied to absorb the blood collection and reduce discolouration.
- Apply firm elastic bandage.
- Shift the patient to the hospital as soon as possible for the medical aid.
(ii) Abrasion:
- Use protective gear like helmet, knee pads, elbow pads, glasses etc. while doing activities.
- Use anti itching cream over and near abrasion area.
- If cut has bleeding, apply gentle pressure with clean cloth. Hold the pressure for 20 to 30
minutes. - Immediately rinse out the wound with clear water, do not use soap over it, it may irritate the wound. Through wound cleaning reduces the risk of tetanus.
- After cleaning the wound, apply antibiotic cream over it to moist the surface.
- Use bandage to keep the wound clean and keep harmful bacteria out.
- Use ice to reduce the swelling.
- Call doctor if scrape is very large and dirty and one is unable to remove debris and dirt, which may cause further infection.
(iii) Strain:
- Strain is firstly treated as PRICE, where ‘P’ stands for ‘protection’ and ‘R’ stands for ‘Rest’, ‘I’ stands for ‘Ice Application’, C stands for ‘Compression’ and ‘E’ stands for ‘Elevation’. The first thing is to immobilize or rest the sprained area. If necessary, use sling for an arm injury or crutches for a leg or foot injury. Apply ice on an injured part for atleast 20 minutes after every hour. Never put ice directly against skin or it may damage the skin.
- Place the patient in a comfortable position.
- Immobilized the injured area.
- Steady and support the injured part.
- Elevate the injure injured part.
- Continue ‘RICE’ for 24 to 48 hours.
- Shift the patient to the hospital or consult doctor.
(iv) Dislocation:
1. Pain Reduction:
During this process, the doctor may try some gentle movements around the affected joint to help the bones back into position. In case of severe pain local anaesthetic procedures are adopted.
2. Immobilization:
After getting the bones at normal position the joint should be immobilized with a splint or sling for several weeks. The time for which sling or splint is to be used depends upon extent of damage to nerves, blood vessels and supporting tissues.
3. Surgery:
If reduction is not able to settle the joint then surgical technique can be used to move dislocated bones back into their correct positions. Even in case of ruptured nearby blood vessels, nerves or ligaments surgery is required.
4. Rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation process is started after the splint or sling is removed. For the dislocated joint the rehabilitation exercises should be designed in such a way that the gradual load is given. The aim of rehabilitation is to restore normal range of motion and strength around the joint.
![]()
Question 9.
What do you know about impact?
Answer:
It is common to suffer from injuries during competitive sports. In order to win at any cost, sportsperson performed with zeal and fast pace in competitions. In this stituation, the players sometimes come directly in contact with other player and causes injury. The common sports activities in which players suffer injuries due to direct impact are kabaddi, wrestling, boxing, football, hockey etc.
Five Marks Question-Answers
Question 10.
Explain the types of fracture in detail.
Answer:
Fracture:
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone. Fracture occurs when the bone is subjected to stress greater than it can absorb. Fracture can be caused by a direct blow, force, sudden twisting motion and even extreme muscles contraction. The causes of fracture can be direct force, indirect force, force of muscular action and force of ligament. There are following types of bone fractures that may occur during playing or due to accident:
1. Closed Fracture/Simple Fracture:
Its simply the break down of bone in two pieces. It does not produce a break in the skin.
2. Open Fracture/Compound Fracture:
It is one in which the skin or mucous membrane wound extends to the fracture bone.
3. Commuted Fracture: A fracture in which bone has splintered into several fragments.
4. Complicated Fracture:
A fracture in which the fractured bone fragment is driven into another organs or ligaments such as fracture in throacic bone may affect lungs etc.
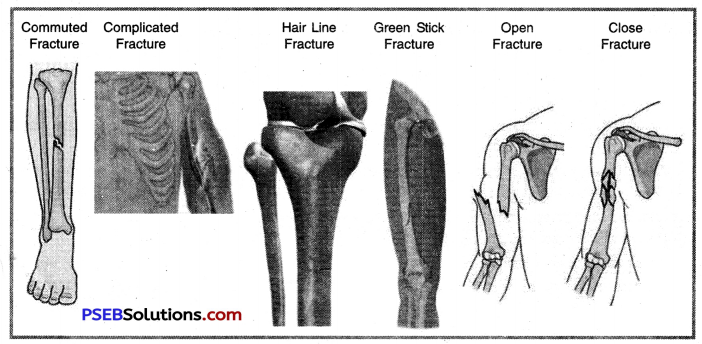
5. Green Stick Fracture:
A fracture in which only one side may get broken and the bone then appears to be bent, but not broken. It is most common in children.
6. Hair line Fracture:
In this type of fracture the thin hair line crack appears in the bone.
7. Depressed Fracture:
A fracture in which fragments are driven inward. This type of fracture can be seen in flat bones such as skull bones etc.
![]()
Question 11.
Describe sports injuries. Also write the reasons of sports injuries.
Answer:
A sports injury may be defined as “damage to the tissues of the body that occurs as a result of sport or exercise”. Sports injuries can be classified according to the cause of the injury or the type of tissues damaged.
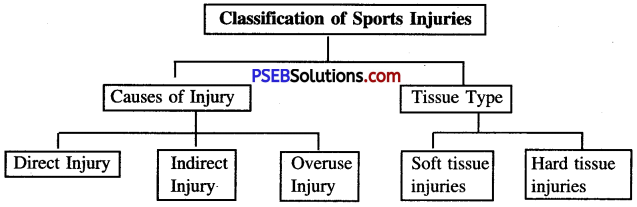
If we divide injury according to the cause then it can be categorised as under:
1. Direct Injury: A direct injury is caused by an external blow or force.
2. Indirect injury:
The injury does not result from physical contact with an object or person, but from internal forces built up by the actions of the performer, such as may be caused by overstretching, poor technique, etc.
3. Overuse injury:
Overuse injuries occur when excessive and repetitive force is placed on the bones and other connective tissues of the body.
If injuries are classified according to the damaged tissues then we can classify them as follows:
1. Soft Tissue Injuries:
Soft-tissue injuries are the most common injuries resulting from participation in sport. It occurs to muscles, tendons, ligaments and the skin. These injuries include sprain, strain, contusion, abrasion, laceration and blisters.
2. Hard Tissue Injuries:
Hard tissue injuries include injuries to bones or around joints i.e., fracture and dislocations.
Reasons of Sports Injuries. Sports injuries are commonly caused due to overuse, over twisting, over stretching, collision, etc. These injuries can be mild to severe. Most of the injuries are caused due to lack of knowledge. Sports injuries can occur on the play field or while playing due to reasons given ahead:
1. Poor Physical Fitness of Player:
Physical fitness is required for better performance. Physical fitness can be achieved with regular practice. All components like strength, speed, flexibility, endurance, agility, power, balance etc must be possess by the athlete. Lack of physical fitness then causes injury.
2. Due to Poor Psychological Preparation:
If athlete is stressful, full of anxiety or may be playing in tension can be injured easily. For prevention of injury, one must be psychologically prepared for the event.
3. Inadequate warming up before match:
Warming-up is very important for the prevention of injuries. The stretching exercises done during the warm-up session often prevent injuries such as sprain and strain. After proper warming up, the body becomes ready to bear any sort of physical stress. That is why it has been always suggested to begin more vigorous activity after having proper warm-up exercises.
4. Lack of knowledge of proper technique:
By using the accurate technique one can reduce the risk of overuse injuries, such as tendonitis and stress fractures. The injuries like tennis elbow are due to improper technique and overuse. If you are unsure about the correct technique, a qualified sports coach can give you advice. If you exercise in a gym or a leisure centre, ask a fitness instructor or member of gym staff for help.
5. By using substandard sports equipment:
Half of the game can be won by using good equipment. Substandard or poor quality equipment causes injuries during match or practice. Hence, it is always recommeded to use quality equipment during game.
6. Lack of knowledge of rules and regulation of game:
The rules are formulated keeping in view the safety of the sportsmen. Rules of conduct, including illegal blocks and tackles are enforced to keep athlete injury free. Many games have rule of “no body contact” to avoid injuries. By playing under discipline the injuries can be prevented.
7. Bad conditions of Play fields:
The equipment and play fields having all safety measures can save lots of sports injuries. For example running on synthetic track as compared to mud track has less chance of injuries. In basketball safety pads on poles can protect injuries.
8. Due to Arrogance of Player:
Sometimes aggressive players intensely injured other players with intension to injure. To avoid such type of injury, they must be punished at the time.
9. Due to Bad Climate:
Bad climates like sudden rain or uneven ground or may be weather condition like severe cold or hot weather can also cause injury sometimes.
10. Due to Lack of Match Practice:
As we know practice makes a man perfect, athlete must be well prepared and practiced before match. Every day match practice is required for coordination, understanding with fellow team mates, conditioned body movements etc for the prevention of injuries.
![]()
Question 12.
Write the meaning and principles of first aid.
Answer:
“First aid is the immediate treatment given to the victim of sudden illness before medical help is made available”. It is applied to prevent further injury, reduce pain experienced by the patient, and shock from the injury. The most important basic concept in first aid is to stop bleeding, restore adequate breathing and treat the patient from shock.
This is very necessary to make sure that the patient has an open airway, is breathing appropriately, and has circulation intact i.e. pulses, normal skin colour and no uncontrolled bleeding. If the patient has stable other specific injuries can be addressed with first aid. The basic concepts of first aid includes keeping wounds clean, applying pressure to stop bleeding and keeping suspected broken bones immobile until they can be evaluated and aligned appropriately.
Principles of First Aid. The basic principles of First aid are as follows:
- Do first thing fast and quickly, quietly and without panic.
- Guard against a treat shock by moving the causality as little as possible.
- Do not attempt too much.
- Reassure the causality and those around in order to reduce tension.
- Give artificial respiration if required.
- Try to stop bleeding.
- Do not allow people around patient as fresh air is required.
- Do not change or remove clothes unnecessarily.
- Arrange immediate vehicle or ambulance to take patient to the hospital.
![]()
PSEB 12th Class Physical Education Guide Sport Injuries Important Questions and Answers
One Mark Question-Answers
Question 1.
Give full form of PRICE.
Answer:
Protection, Rest, Ice application, compression, elevation.
Question 2.
Enlist any two soft tissue injuries.
Answer:
Sprain and contusion.
Question 3.
Write any two hard tissue injuries.
Answer:
Fracture, Dislocation.
Question 4.
What is direct injury?
Answer:
A direct injury is caused by external blow or force.
![]()
Question 5.
Enlist any two causes of sports injury.
Answer:
- Poor physical fitness of player
- Due to inadequate warming up.
Question 6.
Give any two safety measures for injuries.
Answer:
- Preventive Measures.
- Curative Measures.
Question 7.
Highlight two principles of First Aid.
Answer:
(i) Do first thing fast and quickly, quietly and without panic.
(ii) Do not attempt too much.
Question 8.
Define First Aid.
Answer:
First aid is the immediate treatment given to the victim of sudden illness before medical help is made available.
Question 9.
Enlist various types of strain.
Answer:
(i) Acute strain
(ii) Chomic strain.
Question 10.
Give two causes of strain.
Answer:
(i) Excessive stretching.
(ii) Sudden movement.
Question 11.
What are the symptoms of strains? Give any two.
Answer:
(i) Sudden pain, swelling, burning at the site of injury
(ii) Excessive pain during movement.
![]()
Question 12.
What should be the duration of ice application in sprain?
Answer:
20 minutes every hour.
Question 13.
Highlight any two symptoms of contusion.
Answer:
- Burning of the skin
- Localized pain to the injured area.
Question 14.
Enlist various type of Abrasion.
Answer:
Scratches, Grazes, Pressure abrasion, Impact abrasion.
Question 15.
Give any two types of fracture?
Answer:
- Green stick fracture
- Commuted fracture.
Question 16.
What are the symptoms of fracture?
Answer:
- Severe pain
- Swelling around the injured area.
Question 17.
What is chronic strain?
Answer:
A chronic strain results from prolonged repetitive movements of a muscles. This may occur during events for example Gymnastics, Tennis, Rowing and Golf etc.
![]()
Question 18.
How many hours PRICE principle should be applied?
Answer:
24 hours to 48 hours.
Question 19.
What is ordinary sprain?
Answer:
It is mild in nature and little swelling can be seen which has no impact on movements and functions.
Question 20.
What do you mean by laceration?
Answer:
Laceration is the cut over the skin. It is minor wound on skin.
Question 21.
What do you mean by depressed fracture?
Answer:
A fracture in which fragments are driven inward. This type of fracture can be seen in flat bones such as skull bones etc.
Question 22.
What is complicated fracture?
Answer:
A fracture in which the fractured bone fragment is driven into another organs or ligaments such as fracture in throacic bone may affect lungs etc.
![]()
Question 23.
What is commuted fracture?
Answer:
A fracture in which bone has splintered into several fragments.
Two Marks Question-Answers
Question 1.
What are major injuries?
Answer:
These injuries are commonly affect muscles, tendons, skin etc. and major injuries are: Sprain, Strain, Contusion, Abrasion, laceration, bruises, fracture, dislocation.
Question 2.
What do you understand by sprain?
Answer:
A sprain is a tear of ligament fibres, muscles or tendons supporting a joint or it is defined as an injury to the ligament and joint capsule. Sprain occurs when joint is extended beyond its normal range, sudden movement, twisting of the part involving joint.
Question 3.
Write about the principles of First Aid.
Answer:
- Do first thing fast and quickly, quietly and without panic.
- Guard against a treat shock by moving the causality as little as possible.
- Do not attempt too much.
![]()
Question 4.
Enlist various causes of sports injuries.
Answer:
- Poor Physical fitness of player
- Due to poor psychological preparation
- Inadequate warming up before match.
Question 5.
Highlight various soft tissue related injuries.
Answer:
Soft-tissue injuries are the most common injuries resulting from participation in sport. It occurs to muscles, tendons, ligaments and skin. These injuries include sprain, strain, contusion, abrasion, laceration, blisters and incision.
Question 6.
What do you understand by contusion?
Answer:
A contusion or bruise is bleeding into the soft tissue. It is caused by a direct blow from another person or a direct hit by a blunt object. A bruise can occur to any soft tissue of the body. In contusion capillaries are ruptured and swelling, bleeding and pain appear on the injured part.
Question 7.
Elucidate the term abrasion.
Answer:
Abrasion occurs when the outer layer of skin is removed, usually as a result of a scraping action. It may be any grade of severity from a simple scraping away of a layer of skin to very extensive damage. The open wound can contain dirt or gravel, which should be removed to avoid further infection.
![]()
Question 8.
Enlist various types of hard tissue injuries.
Answer:
Hard tissue injuries include injuries to bones or around joints i.e., fracture and dislocations.
Question 9.
Write any two symptoms of dislocation of bones.
Answer:
- Severe pain in the joint.
- Reduction in movement around the joint.
- Joint looks deformed.
- Swelling appears.
Question 10.
What do you understand by the term ‘PRICE’?
Answer:
Protection, Rest, Ice, application, Compression and Elevation.
Question 11.
Elucidate soft tissues injuries.
Answer:
Soft-tissue injuries are the most common injuries resulting from participation in sport. It occurs to muscles, tendons, ligaments and the skin. These injuries include sprain, strain, contusion, abrasion, laceration, blisters and incision.
Question 12.
Differentiate between direct and indirect injury.
Answer:
(a) Direct Injury: A direct injury is caused by an external blow or force.
(b) Indirect injury: The injury does not result from physical contact with an object or person, but from internal forces built up by the actions of the performer, such as may be caused by overstretching, poor technique, etc.
Question 13.
Differentiate between soft tissue and hard tissue injury.
Answer:
Soft Tissue Injuries:
Soft-tissue injuries are the most common injuries resulting from participation in sport. It occurs to muscles, tendons, ligaments and the skin. These injuries include sprain, strain, contusion, abrasion, laceration and blisters.
Hard Tissue Injuries: Hard tissue injuries include injuries to bones or around joints i.e., fracture and dislocations.
![]()
Question 14.
Enlist various principles of First Aid.
Answer:
- Try to stop bleeding.
- Do not allow people around patient as fresh air is required.
- Do not change or remove clothes unnecessarily.
- Arrange immediate vehicle or ambulance to take patient to the hospital.
Question 15.
What are the symptoms of strain?
Answer:
- Burning, pain, and swelling.
- Severe pain during movement.
- Discoloration
- Tenderness.
Question 16.
Give any two reasons of strain.
Answer:
- Over stretching.
- Sudden movement.
Question 17.
What do you know about sprain?
Answer:
A sprain is a tear of ligament fibres, muscles or tendons supporting a joint or it is defined as an injury to the ligament and joint capsule. Sprain occurs when joint is extended beyond its normal range, sudden movement, twisting of the part involving joint.
![]()
Question 18.
Define contusion.
Answer:
A contusion or bruise is bleeding into the soft tissue. It is caused by a direct blow from another person or a direct hit by a blunt object. A bruise can occur to any soft tissue of the body. In contusion capillaries are ruptured and swelling, bleeding and pain appear on the injured part.
Three Marks Question-Answers
Question 1.
What is strain? What are the symptoms of strain?
Answer:
Strain is a disruption of the fibres of a muscle or tendon. Tears or strains occur when a muscle or tendon is over-stretched or when a muscle contracts too quickly. The causes of strain occur while lifting weights, muscles are stretched during sudden jerky motion, landing badly on an ankle or walking or exercising on uneven surface. This type of injury generally causes sprains in knees or ankles.
Sign and symptoms:
- Sudden pain at the site of injury.
- Stifhess and cramps.
- Swelling at the site of injuries and sometime redness also appears.
- Tenderness.
- No movement and numbness.
Question 2.
What are the principles of First Aid?
Answer:
The basic principles of First aid are as follows:
- Do first thing fast and quickly, quietly and without panic.
- Guard against a treat shock by moving the causality as little as possible.
- Do not attempt too much.
- Reassure the causality and those around in order to reduce tension.
- Give artificial respiration if required.
- Try to stop bleeding.
- Do not allow people around patient as fresh air is required.
![]()
Question 3.
How would you give First aid for the sprain?
Answer:
There are few steps for prevention of sprains:
- Sprain is firstly treated as ‘PRICE’, where ‘P’ mean ‘protection’ ‘R’ stands for ‘Rest’, ‘I’ stands for ‘Ice application’, ‘C’ stands for ‘Compresion’ and E stands for ‘Elevation’. Rest the sprained area. If necessary, use sling for an arm injury or crutches for a leg or foot injury. Apply ice on an injured part for 20 minutes every horn. Never put ice directly against skin or it may damage the skin.
- Give comfortable position to the patient.
- Provide support to the injured part.
- Immobilize and elevate the injured part.
- Cold compression is given to reduce swelling.
Question 4.
Enlist various preventive measures of dislocation.
Answer:
1. Reduction:
During this process, the doctor may try some gentle movements around the affected joint to help the bones back into position. In case of severe pain local anaesthetic procedures are adopted.
2. Immobilization:
After getting the bones at normal position the joint should be immobilized with a splint or sling for several weeks. The time for which sling or splint is to be used depends upon extent of damage to nerves, blood vessels and supporting tissues.
3. Surgery:
If reduction is not able to settle the joint then surgical technique can be used to move dislocated bones back into their correct positions. Even in case of ruptured nearby blood vessels, nerves or ligaments surgery is required.
4. Rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation process is started after the splint or sling is removed. For the dislocated joint the rehabilitation exercises should be designed in such a way that the gradual load is given. The aim of rehabilitation is to restore normal range of motion and strength around the joint.
Question 5.
Differentiate between fracture and dislocation.
Answer:
Fracture:
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone. Fracture occurs when the bone is subjected to stress greater than it can absorb. Fracture can be caused by a direct blow, force, sudden twisting motion and even extreme muscles contraction. The causes of fracture can be direct force, indirect force, force of muscular action and force of ligament.
Dislocation;
Dislocation is injury to joints where one bone is displaced from another. A dislocation is often accompanied by considerable damage to the surrounding connective tissues. Dislocation occurs as a result of the joint being pushed past its normal range of movement. Common site occurring of dislocation are finger, shoulder, hip joint and patella.
![]()
Question 6.
Define Abrasion. Also explain various types of Abrasion.
Answer:
Abrasion:
Abrasion occurs when the outer layer of skin is removed, usually as a result of a scraping action. It may be any grade of severity from a simple scraping away of a layer of skin to very extensive damage. The open wound can contain dirt or gravel, which should be removed to avoid further infection.
Types of Abrasions:
Abrasion is four types:
1. Scratches:
An abrasion by sharp or pointed object, not sharp enough to incise but pointed enough to scratches e.g. pin, tip of knife, finger nail etc. Scratches have length but no significant width.
2. Grazes:
Grazes caused by movement between skin and some rough surface in contact with it. They are commonly seen in road accidents.
3. Pressure abrasion:
Caused by crushing of superficial layers of epidermis and are associated with bruise of surrounding area. In this abrasion movement is slightly and directed inward.
4. Impact abrasion:
Caused by impact with a rough object. For example when a person is knocked down by motor car, a headlamps rim or tread of type may be seen on the skin.
Question 7.
Explain various causes of sports injury.
Answer:
Sports injuries are commonly caused due to overuse, over twisting, over stretching, collision, etc. These injuries can be mild to severe. Most of the injuries are caused due to lack of knowledge. Sports injuries can occur on the play field or while playing due to reasons given ahead:
1. Poor Physical Fitness of Player:
Physical fitness is required for better performance. Physical fitness can be achieved with regular practice. All components like strength, speed, flexibility, endurance, agility, power, balance etc must be possess by the athlete. Lack of physical fitness then causes injury.
2. Due to Poor Psychological Preparation:
If athlete is stressful, full of anxiety or may be playing in tension can be injured easily. For prevention of injury, one must be psychologically prepared for the event.
3. Inadequate warming up before match:
Warming-up is very important for the prevention of injuries. The stretching exercises done during the warm-up session often prevent injuries such as sprain and strain. After proper warming up, the body becomes ready to bear any sort of physical stress. That is why it has been always suggested to begin more vigorous activity after having proper warm-up exercises.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the safety measures for sports injury?
Answer:
There are following points which one should consider for safety:
1. Proper Warming Up:
The most important measure to prevent injuries is to perform warming up exercises prior to any event. This would help to prepare an athlete physiologically and psychologically for the event. Hence, the chances of getting injuries would be less by performing proper warming up exercises.
2. According to the fitness level of an athlete:
Sometimes the injury may cause due to overuse of the muscle, in which there are more chances of wear and tear of muscle tissue. So, it is important that the training load should be according to the fitness level of an athlete.
3. Proper technique:
Faulty methods of training or practicing wrong technique would also lead to injury. So, teacher needs to constantly check whether an athlete is practicing appropriate technique or not. It is important to make correction at an early age.
Question 9.
Briefly explain the term RICE and PRICE.
Answer:
RICE:
The term RICE implies ‘R’ means rest, ‘I’ stands for ‘Ice application’ ‘C’ means ‘compression and ‘E’ represents ‘Elevation.’ The term ‘PRICE’ denotes ‘P’ which means ‘protection’ or ‘prevention’ i.e., prevention is better than cure. Hence, principle of ‘PRICE’ most suitable and applicable in the field of sports.
Question 10.
Write a short note on:
(i) Strain
(ii) Contusion.
Answer:
(i) Strain:
Strain is a disruption of the fibres of a muscle or tendon. Tears or strains occur when a muscle or tendon is over-stretched or when a muscle contracts too quickly. The causes of strain occur while lifting weights, muscles are stretched during sudden jerky motion, landing badly on an ankle or walking or exercising on uneven surface. This type of injury generally causes sprains in knees or ankles,
(ii) Contusion:
A contusion or bruise is bleeding into the soft tissue. It is caused by a direct blow from another person or a direct hit by a blunt object. A bruise can occur to any soft tissue of the body. In contusion capillaries are ruptured and swelling, bleeding and pain appear on the injured part.
![]()
Question 11.
Differentiqate between Sprain and Strain.
Answer:
Sprain:
A sprain is a tear of ligament fibres, muscles or te’Jons supporting a joint or it is defined as an injury to the ligament and joint capsule. Sprain occurs when joint is extended beyond its normal range, sudden movement, twisting of the part involving joint.
Strain:
Strain is a disruption of the fibres of a muscle or tendon. Tears or strains occur when a muscle or tendon is over-stretched or when a muscle contracts too quickly. The causes of strain occur while lifting weights, muscles are stretched during sudden jerky motion, landing badly on an ankle or walking or exercising on uneven surface. This type of injury generally causes sprains in knees or ankles.
Five Marks Question-Answers
Question 1.
Elaborate the term dislocation with its symptoms and preventive measures.
Answer: Dislocation. Dislocation is injury to joints where one bone is displaced from another. A dislocation is often accompanied by considerable damage to the surrounding connective tissues. Dislocation occurs as a result of the joint being pushed past its normal range of movement. Common site occurring of dislocation are finger, shoulder, hip joint and patella.
Symptoms:
- Severe pain in the joint.
- Reduction in movement of the joint.
- Joint looks deformed.
- Swelling appears.
Prevention of Dislocation:
As dislocation occurs immediately restrict the joint for further movement. Further movement of dislocated joint can damage the joint and its surrounding muscles, ligaments, nerves or blood vessels. Apply ice on the injured joint. This can help in reducing swelling by controlling internal bleeding.
After this restrict the joint from moving by using a bandage. For an arm injury, a sling can be used to support the arm. For a leg injury, use padding or broad-fold bandages. To give extra support for an injured shoulder, tie a bandage around the arm. After stopping the joint from moving, send the injured person to hospital.
The dislocation is treated by expert doctors. The management of dislocation is done as following steps:
1. Reduction:
During this process, the doctor may try some gentle movements around the affected joint to help the bones back into position. In case of severe pain local anaesthetic procedures are adopted.
2. Immobilization:
After getting the bones at normal position the joint should be immobilized with a splint or sling for several weeks. The time for which sling or splint is to be used depends upon extent of damage to nerves, blood vessels and supporting tissues.
3. Surgery:
If reduction is not able to settle the joint then surgical technique can be used to move dislocated bones back into their correct positions. Even in case of ruptured nearby blood vessels, nerves or ligaments surgery is required.
4. Rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation process is started after the splint or sling is removed. For the dislocated joint the rehabilitation exercises should be designed in such a way that the gradual load is given. The aim of rehabilitation is to restore normal range of motion and strength around the joint.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a short note on:
1. Abrasion
2. Dislocation.
3. Contusion
Answer:
1. Abrasion:
Abrasion occurs when the outer layer of skin is removed, usually as a result of a scraping action. It may be any grade of severity from a simple scraping away of a layer of skin to very extensive damage. The open wound can contain dirt or gravel, which should be removed to avoid further infection.
2. Contusion:
A contusion or bruise is bleeding into the soft tissue. It is caused by a direct blow from another person or a direct hit by a blunt object. A bruise can occur to any soft tissue of the body. In contusion capillaries are ruptured and swelling, bleeding and pain appear on the injured part.
3. Dislocation:
Dislocation is injury to joints where one bone is displaced from another. A dislocation is often accompanied by considerable damage to the surrounding connective tissues. Dislocation occurs as a result of the joint being pushed past its normal range of movement. Common site occurring of dislocation are finger, shoulder, hip joint and patella.
Question 3.
What do you know about strain? Write its symptoms and treatment
Answer:
Soft tissue injuries occur in sports. These are common injuries which mostly occur on the ground while playing the game. These are as under:
(a) Strain/Tear:
Strain is a disruption of the fibres of a muscle or tendon. Tears or strains occur when a muscle or tendon is overstretched or when a muscle contracts too quickly. The causes of strain occur while lifting weights, muscles are stretched during sudden jerky motion, landing badly on an ankle or walking or exercising on uneven surface. This type of injury generally causes sprains in knees or ankles. There are two types of strains.
1. Acute strain
2. Chronic strain
1. Acute Strain:
An acute strain occurs when a muscle become strained or may even tear or when it stretched usually far or abruptly. Acute strains often occur in the following ways:
- Slipping on surface.
- Running, jumping or throwing.
- Lifting a heavy objects.
2. Chronic Strain:
A chronic strain results from prolonged repetitive movements of a muscles. This may occur during events for example Gymnastics, Tennis, Rowing and Golf etc.
Causes of strain
- While lifting weight.
- Sudden movement.
- When muscles are stretched during sudden jerky motion.
Sign and symptoms:
- Sudden pain at the site of injury.
- Stifness and cramps. .
- Swelling at the site of injuries and sometime redness also appears.
- Tenderness.
- No movement and numbness.
Preventions and Remedies:
- Strain is firstly treated as RICE, where ‘R’ stands for ‘Rest’, ‘I’ stands for ‘Ice Application’, C stands for ‘Compression’ and ‘E’ stands for ‘Elevation’. The first thing is to immobilize or rest the sprained area. If necessary, use sling for an arm injury or crutches for a leg or foot injury. Apply ice on an injured part for atleast 20 minutes after every hour. Never put ice directly against skin or it may damage the skin.
- Place the patient in a comfortable position.
- Immobilized the injured area.
- Steady and support the injured part.
- Elevate the injure injured part.
- Continue ‘RICE’ for 24 to 48 hours.
- Shift the patient to the hospital or consult doctor.
![]()
Question 4.
Write about sprain alongwith its symptoms and preventions.
Answer:
Sprain:
A sprain is a tear of ligament fibres, muscles or tendons supporting a joint or it is defined as an injury to the ligament and joint capsule. Sprain occurs when joint is extended beyond its normal range, sudden movement, twisting of the part involving joint. We can grade sprain into three phases:
(i) Ordinary Sprain:
It is mild in nature and little swelling can be seen which has no impact on movements and functions.
(ii) Moderate Sprain: It is moderate, due to swelling and pain it affects the functioning and movements.
(iii) Severe Sprain:
It is pain free sprain as sensory fibres are completely tom up. It has large swelling, loss of functioning generally occurs.
Causes of sprain:
There are few reasons for sprain. They are following:
- Sudden movement.
- Twisting of the part involving joint.
- Over stretch or tear of the ligament supporting that joint.
- Sudden fall on over stretched arm or side of the foot
Sign and Symptoms:
- Burning, pain, and swelling.
- Severe pain during movement.
- Discoloration
- Tenderness.
- Loss of the ability to move.
- Redness or red streaks spreading over injured area.
Prevention and Remedies:
There are few steps for prevention of sprains. .
- Sprain is firstly treated as ‘PRICE’, where ‘P’ stands for ‘protection’ and ‘R’ stands for ‘Rest’, T stands for ‘Ice application’, ‘C’ stands for ‘Compresion’ and E stands for ‘Elevation’. Rest the sprained area. If necessary, use sling for an arm injury or crutches for a leg or foot injury. Apply ice on an injured part for 20 minutes every hour. Never put ice directly against skin or it may damage the skin.
- Give comfortable position to the patient.
- Provide support to the injured part.
- Immobilize and elevate the injured part.
- Cold compression is given to reduce swelling.
- Hot formation is applied to absorb the blood collection and reduce discolouration.
- Apply firm elastic bandage.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you mean about fracture? Write its types.
Answer:
Fracture:
A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone. Fracture occurs when the bone is subjected to stress greater than it can absorb. Fracture can be caused by a direct blow, force, sudden twisting motion and even extreme muscles contraction. The causes of fracture can be direct force, indirect force, force of muscular action and force of ligament. There are ahead types of bone fractures that may occur during playing or due to accident:
1. Closed Fracture/Simple Fracture:
Its simply the break down of bone in two pieces. It does not produce a break in the skin.
2. Open Fracture/Compound Fracture:
It is one in which the skin or mucous membrane wound extends to the fracture bone.
3. Commuted Fracture: A fracture in which bone has splintered into several fragments.
4. Complicated Fracture: A fracture in which the fractured bone fragment is driven into another organs or ligaments such as fracture in throacic bone may affect lungs etc.
5. Green Stick Fracture:
A fracture in which only one side may get broken and the bone then appears to be bent, but not broken. It is most common in children.
6. Hair line Fracture: In this type of fracture the thin hair line crack appears in the bone.
7. Depressed Fracture:
A fracture in which fragments are driven inward. This type of fracture can be seen in flat bones such as skull bones etc.
Signs and Symptoms:
Signs of a fractured bone include one or more of the symptoms which are listed below. Intense pain at the site of the injury that worsens with movement.
- Severe pain
- Swelling around the injured area.
- Bone may protrude through the skin.
- Heavy bleeding may occur at the injury site.
Remedies and Prevention:
Fractured bones are generally not life frightening, but they need instant medical care
1. In case of bleeding apply pressure to the wound with a sterile bandage, a clean cloth, or a clean piece of clothing. Even first aid treatment for shock is also required.
2. In case the injured person has symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, pale and clammy skin, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate. The person should lie quietly with the feet elevated about 12 inches.
3. Cover him or her with a blanket to maintain body warmth. After this immobilize the injured area.
4. Do not let the injured move if there is a back or neck injury. Make a splint by folding a piece of cardboard or newspaper or a magazine, then placing it gently under the limb. Carefully tie the splint to the injured area with pieces of cloth.
5. Cold compression to the injured area also minimizes swelling and faster recovery. Make sure to place a cloth between the skin and the ice to prevent the damage of the skin.
6. If an injured person is unresponsive and is facing great difficulty in breathing can be given CPR. Don’t move the person to avoid further injury.
7. Immobilize the injured area. Apply a splint to the area above and below the fracture sites. Padding the splints can help reduce discomfort.
Question 6.
What do you understand by Sports injuries? Tell about the prevention of Sports injuries.
Answer:
A sports injury may be defined as ‘ ‘damage to the tissues of the body that occurs as a result of sport or exercise”. Sports injuries can be classified according to the cause of the injury or the type of tissues damaged.
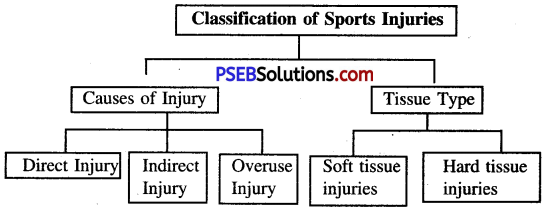
If we divide injury according to the cause then it can be categorised as under:
1. Direct Injury: A direct injury is caused by an external blow or force.
2. Indirect injury:
The injury does not result from physical contact with an object or person, but from internal forces built up by the actions of the performer, such as may be caused by overstretching, poor technique, etc.
3. Overuse injury:
Overuse injuries occur when excessive and repetitive force is placed on the bones and other connective tissues of the body.
If injuries are classified according to the damaged tissues then we can classify them as follows:
1. Soft Tissue Injuries:
Soft-tissue injuries are the most common injuries resulting from participation in sport. It occurs to muscles, tendons, ligaments and the skin. These injuries include sprain, strain, contusion, abrasion, laceration and blisters.
2. Hard Tissue Injuries:
Hard tissue injuries include injuries to bones or around joints i.e., fracture and dislocations.
Prevention of Sports Injuries. The Physical Education Programme includes the bodily movement where the risks associated with the injury deemed to be acceptably very high. So, it is the responsibility of all the teachers, worker and trainers of Physical Education Programme to identity those risks and situation where the students are not safe in terms of Physical injuries. The Physical Education teacher should make the sports situations and environment safe for the students.
He should also teach safe practices, self safety and effective management of risks to the students. The concept self safety includes various means and ways which helps an athlete to protect him from the chances of injury while playing. It is to gain proper knowledge about the athletic care and how to minimize chances of injury while taking part in games and sports. So, we can say that self safety is a set of measures, ways and methods to care our body from various hazards while participating in games and sports to improve performance. Safety or athletic care has two aspects:
1. Preventive aspects:
It guides us about the preventive ways of the problems.’i.e. how we should prevent ourselves from injury, accident or other hazards. It guides us about preventive clothing, protective equipment, safety equipment, rest and diet etc.
2. Curative aspects:
It guide us how to cure, manage and give treatment to injury. This includes corrective exercise and rehabilitation programme to manage and recover from the injury.
There are following preventive measures which one should consider for safety:
1. Proper Wanning Up:
The most important measure to prevent injuries is to perform warming up exercises prior to any event. This would help to prepare an athlete physiologically and psychologically for the event. Hence, the chances of getting injuries would be less by performing proper warming up exercises.
2. According to the fitness level of an athlete:
Sometimes the injury may cause due to overuse of the muscle, in which there are more chances of wear and tear of muscle tissue. So, it is important that the training load should be according to the fitness level of an athlete.
3. Proper technique:
Faulty methods of training or practicing wrong technique would also lead to injury. So, teacher needs to constantly check whether an athlete is practicing appropriate technique or not. It is important to make correction at an early age.
4. After complete recovery from an injury:
Sometimes athletes start practicing after incomplete recovery from the previous injury, this would lead to further complications and chances of injuries increase in this condition. Hence, an athlete must participate after the complete recovery to avoid further chances of injuries.
5. Safety of equipment:
The most important aspect in the teaching of skill to the students of physical education is that the teacher must have relevant knowledge about the group he is going to deal with it a class. The key information regarding the students includes their physical, mental and physiological capacities and capabilities. Teacher needs to constantly check whether the place (field) where they are going to perform the activity is safe or not. The second concern should be the equipment they are going to use should be properly checked prior to an activity. The equipment you are going to use while participating in sports and other activities is key to injuries.
6. Handling dangerous equipment:
The activity which involves the use of dangerous equipment like javelin, shot-put, hockey stick etc., special attention should be given in the placement of students in the field. No one should be allowed to trespass or cross the field during the use of such equipment.
7. Use of protective equipment:
The activities involving chances of physical injury due to bodily or equipment contact must be performed while using protective equipment. The protective equipment such as head guard, gun shield, cup protective, anklet, knee guard, chest guard etc. must be worn while taking part in sports such as boxing, hockey goal keeping and other contact sports.
Hence, it can be concluded from the above facts that the teachers who are managing and conducting the physical training programme must realize the importance of safety measures in terms of equipment.
![]()
Question 7.
Elucidate First Aid. Write down principles of First Aid.
Answer:
“First aid is the immediate treatment given to the victim of sudden illness before medical help is made available”. It is applied to prevent further injury, reduce pain experienced by the patient, and shock from the injury. The most important basic concept in first aid is to stop bleeding, restore adequate breathing and treat the patient from shock.
This is very necessary to make sure that the patient has an open airway, is breathing appropriately, and has circulation intact i.e. pulses, normal skin colour and no uncontrolled bleeding. If the patient has stable other specific injuries can be addressed with first aid. The basic concepts of first aid includes keeping wounds clean, applying pressure to stop bleeding and keeping suspected broken bones immobile until they can be evaluated and aligned appropriately.
Principles of First Aid
The basic principles of First aid are as follows:
- Do first thing fast and quickly, quietly and without panic.
- Guard against a treat shock by moving the causality as little as possible.
- Do not attempt too much.
- Reassure the causality and those around in order to reduce tension.
- Give artificial respiration if required.
- Try to stop bleeding. .
- Do not allow people around patient as fresh air is required.
- Do not change or remove clothes unnecessarily.
- Arrange immediate vehicle or ambulance to take patient to the hospital.
Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Physical Education Book Solutions Chapter 4 Sport Injuries Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.