PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Physical Education Chapter 1 Physical Fitness
Physical Education Guide for Class 12 PSEB Physical Fitness Textbook Questions and Answers
One Mark Question-Answers
Question 1.
How many types of strength are there? Name them.
Answer:
There are two types of strength:
- Dynamic strength
- Static strength.
Question 2.
How many components of Physical fitness are there? Name them.
Answer:
- Strength
- Endurance
- Speed
- Flexibility
- Agibity
- Coordinaiton ability
![]()
Question 3.
Name short term races.
Answer:
100mt., 200 mt., 400 mt., 4 x 100 m Relay, 4 x 200 mt. Relay, 110 mt hurdle, 100 mt hurdle.
Question 4.
Which type of flexibility is more Active flexibility or Passive flexibility?
Answer:
Passive flexibility is more than active flexibility.
Two Marks Question-Answers
Question 5.
What is medium term endurance?
Answer:
It can be required for such activities which lasts from 2 to 10 min. Middle term endurance depends on muscle endurance and speed endurance Middle distance races are the example of the middle term endurance (800 mt., 1500 m) etc.
Question 6.
What do you know about long term endurance?
Answer:
It depends upon the aerobic energy system. Long term endurance can be developed for such an event which lasts for 10 min or more. Marathon, 5000 m and 10,000 m races are the examples of the long term endurance.
Question 7.
What do you know about passive flexibility?
Answer:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with wider range and some external helps. For example, stretching exercise with the help of a partner. This flexibility is more than active flexibility.
![]()
Three Marks Question-Answers
Question 8.
What are the different types of Endurance? Explain each of them in detail.
Answer:
As per the requirements following are the categories of endurance
1. As per the Nature of the Activity:
(a) Basic Endurance:
Basic endurance mainly depends upon aerobic endurance. It is done in slow pace where all the muscle groups of the body are involved in a particular movement. Running, jogging, walking and swimming are the examples of basic endurance.
(b) General Endurance:
It depends upon both aerobic and anaerobic activities. It, is done in both slow and fast pace activities. This enables sportsperson to work for longer duration without any tiredness.
(c) Specific Endurance:
Specific endurance can be differ from sports to sports. Every sport has their own intensity. For example, marathon runners have to run long hours beside boxers have to complete their bout in 3 minute round.
2. As per the Duration of the Activity:
(a) Short Term Duration:
Exercises for short distance can be fixed with the rest interval of short duration. It lasts upto 2 minutes and also called anaerobic activities. Short term endurance is required to resist fatigue in sports activities such as sprints and middle distance races.
(b) Middle Term Endurance:
It can be required for such activities which lasts from 2 to 10 min. Middle term endurance depends on muscle endurance and speed endurance Middle distance races are the example of the middle term endurance (800 mt., 1500 m) etc.
(c) Long Term Endurance:
It depends upon the aerobic energy system. Long term endurance can be developed for such an event which lasts for 10 min or more. Marathon, 5000 m and 10,000 m races are the examples of the long term endurance.
![]()
Question 9.
Write a note on each of the following:
(i) speed
(ii) flexibility
(iii) co-ordinative ability.
Answer:
(i) Speed:
Speed is maximum rate at which a person is able to move his body over a specific distance. We can say that speed is the ability to move from one place to another in the shortest possible time. This ability is mainly hereditary in nature. That is why we can improve speed after rigorous training upto 20% only. It is also said that sprinters are bom not made.
Types of Speed:
1. Reaction Speed: It is the ability to give a quick reaction on a signal. The sportsperson respond against the situation demand.
2. Acceleration Speed:
It is the ability to achieve maximum speed from stationary position. We can see it in sprints. Indirectly .this ability depends on the other factors like explosive strength, technique and flexibility.
3. Movement Speed:
It is the ability to do maximum movement in minimum time. These can be seen in team games, combative sports, racket sports, throws and gymnastics etc.
4. Locomotor Ability:
This is the ability to maintain the speed after accelerated maximally. This can be seen in few events such as short distance races, i.e. 100 m, 200 m and 400 m etc.
5. Speed Endurance:
It is the ability to maintain near maximal speed for a longer duration.
(ii) Flexibility:
Flexibility is the range of movement possible around a joint. In general terms, flexibility has been defined as the range of motion around a joint and its surrounding muscles during passive movements.
Types of Flexibility:
1. Static Flexibility:
It is the ability to extend various joints in a stationary position.
(a) Passive Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with wider range and some external helps. For example, stretching exercise with the ‘ help of a partner. This flexibility is more than active flexibility.
(b) Active Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform flexibility or extension movements with larger amplitude without any external help or a partner. For example, swinging of legs.
2. Dynamic Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with greater amplitude when the body is in motion. Dynamic flexibility is more specific to sports to sports movements. For example, running and somersault in gymanastics or diving in swimming etc.
(iii) Coordination Ability:
Coordination Ability is the ability to perform smooth and accurate motor task, often involving the use of the sense organs and series of correlated muscular contraction that affect a range of joint and therefore relative limb and body position. It depends on the neuro-muscular coordination of the body.
Types of Coordination Ability:
There are mainly seven types of coordinative abilities considered in sports. These are as follows:
1. Orientation Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to analyze and change his body position and its parts in time and space in relation to performance required. For example, gymnast changes his body position as per the requirements of sports performance and basket ball player changes his position from offense to defence as the ball possession goes to opponent.
2. Coupling Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to systematically and meaningfully combine the movement of different body parts for successful performance of sports movement. For example, during spiking in volleyball, the player jumps and hits the ball.
3. Differentiation Ability:
It is the ability which enables the sportsman to separate the different body position and its parts during execution of motor action with high accuracy and movement economy. For example, in volley ball when player jumps for spiking, but drops ball according to the situation.
4. Reaction Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to respond quickly to a given signal and perform the movement in well directed manner. For example, in 100 m sprint when an athlete gets the signal he reacts quickly and performs the movement in desired direction.
5. Balance Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to maintain the dynamic condition. For example, in 400 m race, runner should run in his own lane.
6. Rhythm Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to understand the rhythm of movement and to execute the movement with required rhythm. For example, taking lay-up shot in basketball.
7. Adaptation Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to bring about an effective change in the movement according to anticipated change in the situation. For example, adaptation of scoop to the hitting a ball in hockey.
Five Marks Question-Answers
Question 10.
What do you know about the importance of Physical fitness? Explain in detail.
Answer:
People who are physically fit are able to enjoy their life to the fullest. In today’s scenario of technological development people hardly spend time for their physical fitness. Now, question arises why it is important to be physically fit. The answer lies in the following points:
1. Improves Overall Health:
Physically fit persons possess numerous health advantages such as respiratory, cardiovascular health and overall functioning of the body remain in active state. This helps, in reducing the chances of type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, reduces risk of some cancer and lastly helps in maintaining good health and wellness.
2. Weight Management:
As we all know that the person with over weight or obese people are more prone to health related problems such as high BP, Ghotestrol level, diabetes etc. So, people who are living active lifestyle and physically fit are less likely to face these problems as they are able to control and manage their optimum weight with the help of regular exercise and stay fit.
3. Importance as a stress management:
Through the physical fitness and wellness programme, an individual become capable of managing stress, releiving stress and easily distracted from the daily stresses. Hence, this help in staying active and balanced in any stage of life. So, in order to maintain relaxed state of mind, a person should be physically fit.
4. Reduced risk of injuries:
Physical fitness prevents the chances of injuries in later stage. The reason for the same could be the increased muscle strength, bone density, flexibility and stability. It reduces the chances of injuries especially, as a person get older e.g. strong bones mean less likely to suffer bone injuries as later age.
5. Increases life expectancy:
Regular exercise and physical acitivity reduces the chances of health related diseases, which increases life expectancy and reduce the risk of premature mortality. It has been observed that people who are more active tend to be healtheir and tend to live longer.
6. Proper growth and development:
Through fitness and wellness programme children tend to grow and develop better. They are able to attain good shape, height, structure and optimum weight with the help of their physical fitness programme. So, physically fit person are in well balanced state of their physical structure as well.
7. Improves work efficiency:
The person who are physically fit are tend to perform well in every sphere of life such as work place, family peer group etc. Due to their active and balance state of body and mind their output at work place is more and they tend to enjoy social group with more zeal and excitement. Hence, helps in enjoying their life to the fullest.
Hence, it can be concluded that physical fitness is important for the ‘‘Sound mind in a sound body”. To enjoy at every stage of life.
![]()
Question 11.
Write the meaning and definition of Physical fitness.
Answer:
Physical fitness is one of the basic requirements of life. It is the ability to carry out our daily tasks without undue fatigue. It is also refer to balanced state of psychological, physiological or anatomical aspects of the person. The concept of physical fitness, in the field of physical education and sports, means the capability of an individual to meet the varied physical and physiological demands made by a sporting activity, without reducing the person to an excessively fatigued state. Such a state would be one in which individual can no longer perform the skills of the activity accurately and successfully.
It is necessary for every individual to be physically fit to perform their daily work with ease or without undue fatigue and to take part in various activities effectively. Everyone should be fit enough through participation in physical activities to develop the different components related to physical fitness.
1. According to Clarke:
“Physical fitness is the ability to carry out daily task with vigour and alertness without undue fatigue and ample energy to enjoy leisure time pursuits and to meet unforeseen emergencies.”
2. According to Bucher and Prentice:
“Physical fitness is organic development, muscular strength and stamina. Physical fitness implies efficient performance in exercises.”
3. According to Thomas: “Physical fitness is the total fundamental capacity of an individual to perform a given task”.
4. According to Mathews: “Physical fitness is the capacity of an individual to perform given physical tasks involving muscular effort”.
5. According to William: “Physical fitness is the capacity of an individual to perform physical work”.
6. According to Hubert Dhanaraj: “Physical fitness refers to the ability of the body to tolerate stress in all its kinds and maintain manifestations”.
7. According David R. Lamb: “Physical fitness is the capacity to meet the present and potential physical challenges of life with success.”
8. According to Web Encyclopaedia: ‘‘It is the ability of a person to do daily routine work without fatigue; moreover to participate in playful activity and still reserves enough capacity to meet any emergency.”
Hence, it is important for everyone to stay fit and healthy to perform his daily routine work effectively, to enjoy his life to fullest.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain the factors affecting Physical fitness in detail.
Answer:
There are enormous factors which affects physical fitness in certain ways. Due to inactivity, both short term and long term physical fitness get affected in number of ways. These factors which affect physical fitness are as below:
1. Anatomical Structure:
Anatomical/body structure of every individual is different or they have different shape and sizes. Inappropriate shape and size always hinder in physical performance. Sometimes, genetic impaired organ limits the physical performance of an individual, e.g. a person with smaller lower limbs have more balance as compare to vice-versa.
2. Physiological Structure:
Our all internal system like respiratory system, circulatory system, muscular system and other body systems must work efficiently. Any malfunctioning in systems can affect the physical performance of an individual Example would be problem in breathing or heart diseases etc. may affect the endurance capacity of a person. Hence, for the optimal physical fitness an individual must be physiologically fit also.
3. Psychological Factor:
There are so many psychological disorders which has affect on physical performance e.g. stress, tension, anxiety etc. which are big barriers in performance. Mentally strong and stress free individual can be fit for sports. Stress and tension always limits the physical fitness of a person and hence, affects the performance.
4. Heredity and Environment:
Both, heredity and environment affects physical fitness of an individual. Heredity and environment interacts to produce their effects. This means that the way genes act depends on the environment in which they act. e.g. if any person is a good sportsman, the child tend to have some traits of physical domain. Similarly, environmental variables also effects an individual e.g. difference of height in Japanese and AmericAnswer:
5. Good Posture:
Postural deformities always creates hinderance in physical fitness, for example muscle imbalance, pain, nutrition deficiency, lordosis, scoliosis, round shoulder, knock knees etc. can affect physical fitness of a person, e.g. A person with flat feet would not be able to perform better in events demanding speed.
6. Diet:
Diet plays a major role in physical performance and it is required to maintain physical fitness level. Right amount of calories and nutrition will help athlete to perform their best. Without adequate carbohydrate and fluid, an athlete gets tired very easily and quickly. Protein is needed to rebuild muscles. Without carbohydrates, protein, vitamins athlete will not perform well and it also decreases physical fitness.
7. Life Style:
A person who follow good life style are more fit and perform better in physical performance. Life style does not mean luxuries living; it means living with good habits. An individual who is habitual of smoking, liquor, drug etc. cannot perform well on these components of physical fitness. It affects physical fitness and overall health of a person.
8. Climate:
Different climatic conditions always affects the physical fitness of a person. There are different climatic conditions like winter, summer, humid etc. which influence physical fitness. For better physical performance one must trained themselves in different climate conditions. For example if an individual belongs to the hot and humid area and they have to compete in cold area then, it affects their physical performance. To avoid these barriers one must practice in different climates.
9. Inactivity:
Lack of physical activity leads individual towards sedentary life style which also creates malfunctioning in body system. Physical activity is the term used to describe any kind of everyday activity where body’s movement bums calories. Example would be walking, running, cycling, swimming, sweeping or other household work. Due to inactivity body system gets weaken and other health issues arises.
10. Injury:
Injuries are part of sports. Lack of injury management can decrease performance as well as it affects psychologically on athletes’ mind. Severe or long term injuries often affecting more mentally then physically. Long term injuries leads to inactivity which ultimately affects the physical fitness of a person.
11. Age:
Age differences always affects physical fitness of an individual. As we cannot compare the physical efficiency of an adult with younger ones. In the same way when we grow older, our muscle mass decreases and body fat increases which really affects physical fitness.
12. Gender:
Gender plays a major role in physical performance. Both male and female have huge structural differences. For example female bodies are less muscular, but their joints are more flexible, which gives them greater range of motion and they have an advantage in sports such as gymnastics. Men have larger skeletal muscles as well as larger heart, which generate more power, strength, speed and endurance.
13. Healthy environment:
A healthy environment at school, home or at playfield is helpful in better physical health and fitness. It also encourages athlete to get best physical performance. A healthy environment and good participation is essential for proper rowth and development which plays a key role in physical fitness.
![]()
PSEB 12th Class Physical Education Guide Physical Fitness Important Questions and Answers
One Mark Question-Answers
Question 1.
Enlist any two types of speed.
Answer:
Reaction Speed, Acceleration Speed.
Question 2.
In how many types endurance can be divided?
Answer:
Two types.
Question 3.
Give various types of strength.
Answer:
(i) Dynamic Strength
(ii) Static Strength.
Question 4.
At what age weight training programme should be started?
Answer:
At the age of 18 years.
Question 5.
Enlist any two importance of physical fitness.
Answer:
(i) Improves overall health.
(ii) Weight management.
![]()
Question 6.
Give various components of physical fitness.
Answer:
Strength, Speed, Flexibility, Agility, Balance and Coordination ability.
Question 7.
What is the other name for dynamic strength?
Answer:
Isotonic Strength.
Question 8.
Give substitute name for static strength.
Answer:
Isometric Strength.
Question 9.
What is balance?
Answer:
The ability to control the body position, either stationary or in movement is termed as balance.
Question 10.
Name various types of flexibility.
Answer:
(i) Static flexibility.
(ii) Dynamic flexibility.
Question 11.
Enlist any two coordination abilities.
Answer:
(i) Orientation ability
(ii) Coupling Ability
![]()
Question 12.
Give any two methods for developing agility.
Answer:
- Shuttle Run
- Speed Ladder Agility Drill.
Question 13.
How does William express his views about physical fitness?
Answer:
According to William, “Physical fitness is the capacity of an individual to perform physical work”.
Question 14.
What is strength?
Answer:
The extent to which muscles can exert force by contracting against resistance is known to be strength. In simple words its an ability to work against resistance.
Question 15.
Define strength in the words of Muller.
Answer:
According to Muller,” Strength may be defined as “The force, a muscle can exert against a resistance in one maximal effort”. It is measured in units of pounds or kilograms.”
Question 16.
How does Mathews define strength?
Answer:
According to Mathews,” Muscular Strength is the force that a muscle or group of muscles can exert against a resistance in one maximum effort.”
![]()
Question 17.
What is static strength?
Answer:
It is the ability of muscles to act against resistance without changing or shortening the length, e.g. Pushing against wall in which muscles develops tension without changing its length.
Question 18.
Tell about explosive strength.
Answer:
It is the combination of speed and strength. It is the ability to overcome resistance with high speed. Explosive strength can be seen in sprint races, weight lifting, hammer throw, long jump and high jump etc.
Question 19.
Explain about strength endurance.
Answer:
It is the combination of strength and endurance. It is the ability to overcome resistance for a longer duration. Long distance races, swimming and cycling are the examples of strength endurance.
Question 20.
Whether the muscle changes its length in static strength?
Answer:
No.
Question 21.
What is basic endurance?
Answer:
Basic endurance mainly depends upon aerobic endurance. It is done in slow pace where all the muscle groups of the body are involved in a particular movement. Running, jogging, walking and swimming are the examples of basic endurance.
Question 22.
What is general endurance?
Answer:
It depends upon both aerobic and anaerobic activities. It is done in both slow and fast pace activities. This enables sportsperson to work for longer duration without any tiredness.
![]()
Question 23.
General endurance is part of which type of endurance.
Answer:
Nature of the activity.
Question 24.
If a boxer has to complete for three minutes boxing round, then which type of endurance is required?
Answer:
Specific endurance.
Question 25.
What is the meaning of aerobic?
Answer:
Aerobic means when the oxygen demand is meet during exercise and practice.
Question 26.
Explain middle term endurance in your own words.
Answer:
It can be required for such activities which lasts from 2 to 10 min. Middle term endurance depends on muscle endurance and speed endurance Middle distance races are the example of the middle term endurance (800 m, 1500 m) etc.
Question 27.
In which type of races short term endurance is required?
Answer:
100 mt., 200 mt., 400 mt. etc.
Question 28.
The activities which that end from 2 minutes 10 minutes, what type of endurance is required for these activities.
Answer:
Middle term endurance.
Question 29.
Which type of endurance is required in 5000 and 10000 metre races?
Answer:
Long term endurance.
![]()
Question 30.
Middle term of endurance is part of which types of endurance?
Answer:
Endurance on the basis of duration of activity.
Question 31.
What percentage of speed can be improved after stermous training?
Answer:
Upto 20%.
Question 32.
What do you mean by locomoter ability?
Answer:
This is the ability to maintain the speed after accelerated maximally. This can be seen in few events such as short distance races, i.e. 100 m, 200 m and 400 m etc.
Question 33.
What is speed endurance?
Answer:
It is the ability to maintain near maximal speed for a longer duration.
Question 34.
Which component of physical fitness is improved with shuttle run, polymetric jump and tuck jumps.
Answer:
Agility.
Question 35.
What is adaptation ability?
Answer:
It is the ability of an individual to bring about an effective change in the movement according to anticipated change in the situation. For example, adaptation of scoop to the hitting a ball in hockey.
![]()
Two Marks Question-Answers
Question 1.
Define physical fitness.
Answer:
According to Bucher and Prentice, “Physical fitness is organic development, muscular strength and stamina. Physical fitness implies efficient performance in exercises.”
Question 2.
Give any two importance of physical fitness.
Answer:
1. Improves Overall Health:
Physically fit persons possess numerous health advantages such as respiratory, cardiovascular health and overall functioning of the body remain in active state. This helps in reducing the chances of type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, reduces risk of some cancer and lastly helps in maintaining good health and wellness.
2. Weight Management:
As we all know that the person with over weight or obese people are more prone to health related problems such as high BP, Chotestrol level, diabetes etc. So, people who are living active lifestyle and physically fit are less likely to face these problems as they are able to control and manage their optimum weight with the help of regular exercise and stay fit.
Question 3.
Define Endurance.
Answer:
According to Barrow and McGee, “Endurance is the result of a physiological capacity of the individual to sustain movement over a period of time”.
Question 4.
What do you mean by explosive strength?
Answer:
It is the combination of speed and strength. It is the ability to overcome resistance with high speed. Explosive strength can be seen in sprint races, weight lifting, hammer throw, long jump and high jump etc.
Question 5.
Enlist various factors affecting physical fitness.
Answer:
- Anatomical Structure
- Physiological Structure
- Psychological Factor
- Heredity and Environment
![]()
Question 6.
Define Speed.
Answer:
According to Johnson and Nelson, “speed is the rate at which a person can propel his body or parts of his body through space”.
Question 7.
What do you mean by strength endurance?
Answer:
It is the combination of strength and endurance. It is the ability to overcome resistance for a longer duration. Long distance races, swimming and cycling are the examples of strength endurance.
Question 8.
Enlist two factors affecting physical fitness.
Answer:
Psychological Factor:
There are so many psychological disorders which has affect on physical performance e.g. stress, tension, anxiety etc. which are big barriers in performance. Mentally strong and stress free individual can be fit for sports. Stress and tension always limits the physical fitness of a person and hence, affects the performance.
Diet:
Diet plays a major role in physical performance and it is required to maintain physical fitness level. Right amount of calories and nutrition will help athlete to perform their best. Without adequate carbohydrate and fluid, an athlete gets tired very easily and quickly. Protein is needed to rebuild muscles. Without carbohydrates, protein, vitamins athlete will not perform well and it also decreases physical fitness.
![]()
Question 9.
What points should be taken into consideration while perparing fitness programme?
Answer:
Age:
Age differences always affects physical fitness of an individual. As we cannot compare the physical efficiency of an adult with younger ones. In the same way when we grow older, our muscle mass decreases and body fat increases which really affects physical fitness.
Gender:
Gender plays a major role in physical performance. Both male and female have huge structural differences. For example female bodies are less muscular, but their joints are more flexible, which gives them greater range of motion and they have an advantage in sports such as gymnastics. Men have larger skeletal muscles as well as larger heart, which generate more power, strength, speed and endurance.
Question 10.
What is the meaning of strength endurance?
Answer:
It is the combination of strength and endurance. It is the ability to overcome resistance for a longer duration. Long distance races, swimming and cycling are the examples of strength endurance.
Question 11.
What do you understand by speed and strength?
Answer:
Speed: Speed is maximum rate at which a person is able to move his body over a specific distance.
Strength. It is defined as the force exerted by muscles during a single maximal muscular contraction.
Question 12.
What are the factors affecting physical fitness?
Answer:
1. Anatomical Structure:
Anatomical/body structure of every individual is different or they have different shape and sizes. Inappropriate shape and size always hinder in physical performance. Sometimes, genetic impaired organ limits the physical performance of an individual, e.g. a person with smaller lower limbs have more balance as compare to vice-versa.
2. Psychological Factor:
There are so many psychological disorders which has affect on physical performance e.g. stress, tension, anxiety etc. which are big barriers in performance. Mentally strong and stress free individual can be fit for sports. Stress and tension always limits the physical fitness of a person and hence, affects the performance.
![]()
Question 13.
Define reaction speed.
Answer:
It is the ability to give a quick reaction on a signal. The sportsperson respond against the situation demand.
Question 14.
What is agility?
Answer:
The ability to perform a series of explosive movements in rapid succession in opposing directions (zig-zag running shuttle run or cutting movement). In other words, it can be termed as how quickly a person respond to a given stimulus.
Question 15.
Give any one definition of physical fitness.
Answer:
According David R. Lamb, “Physical fitness is the capacity to meet the present and potential physical challenges of life with success.”
Question 16.
Enlist any two elements of physical fitness.
Answer:
Strength:
The extent to which muscles can exert force by contracting against resistance is known to be strength. In simple words its and ability to work against resistance.
Agility: It is the ability to move and change direction and position of the body quickly and effectively while under control.
Question 17.
Elaborate the term anatomical structure.
Answer:
Anatomical/body structure of every individual is different or they have different shape and sizes. Inappropriate shape and size always hinder in physical performance. Sometimes, genetic impaired organ limits the physical performance of an individual, e.g. a person with smaller lower limbs have more balance as compare to vice-versa.
![]()
Question 18.
Does injuries affects physical fitness and why?
Answer:
Yes, because injuries are part of sports. Lack of injury management can decrease performance as well as it affects psychologically on athletes’ mind. Severe or long term injuries often affecting more mentally then physically. Long term injuries leads to inactivity which ultimately affects the physical fitness of a person.
Question 19.
How does healthy environment affects the physical fitness of a person?
Answer:
A healthy environment at school, home or at playfield is helpful in better physical health and fitness. It also encourages athlete to get best physical performance. A healthy environment and good participation is essential for proper growth and development which plays a key role in physical fitness.
Question 20.
Explain about general endurance and middle term endurance.
Answer:
General Endurance:
It depends upon both aerobic and anaerobic activities. It is done in both slow and fast pace activities. This enables sportsperson to work for longer duration without any tiredness.
Middle Term Endurance:
It can be required for such activities which lasts from 2 to 10 min. Middle term endurance depends on muscle endurance and speed endurance Middle distance races are the example of the middle term endurance (800 m, 1500 m) etc.
Question 21.
What is the difference between reaction speed and movement speed?
Answer:
Reaction Speed:
It is the ability to give a quick reaction on a signal. The sportsperson respond against the situation demand.
Movement Speed:
It is the ability to do maximum movement in minimum time. These can be seen in team games, combative sports, racket sports, throws and gymnastics etc.
![]()
Question 22.
Write in your own words about locomotor speed and accleration speed.
Answer:
Locomotor speed:
This is the ability to maintain the speed after accelerated maximally. This can be seen in few events such as short distance races, i.e. 100 m, 200 m and 400 m etc.
Acceleration Speed:
It is the ability to achieve maximum speed from stationary position. We can see it in sprints. Indirectly ,this ability depends on the other factors like explosive strength, technique and flexibility.
Three Marks Question-Answers
Question 1.
Differentiate between Isotonic and Isometric strength.
Answer:
Dynamic Strength or Isotonic Strength:
When the contraction results in the change of muscles length and the pressure remains same throughout the contraction, it can be called dynamic strength. For example, involving movement at more than one joint i.e. push ups, pull-ups, barbell press, squats, lunges and dead lifts etc. Dynamic strength can also be divided in three parts:
Static strength or Isometric strength:
It is the ability of muscles to act against resistance without changing or shortening the length, e.g. Pushing against wall in which muscles develops tension without changing its length.
![]()
Question 2.
How would you classify endurance on the basis of nature of activity?
Answer:
1. Basic Endurance:
Basic endurance mainly depends upon aerobic endurance. It is done in slow pace where all the muscle groups of the body are involved in a particular movement. Running, jogging, walking and swimming are the examples of basic endurance.
2. General Endurance:
It depends upon both aerobic and anaerobic activities. It is done in both slow and fast pace activities. This enables sportsperson to work for longer duration without any tiredness.
3. Specific Endurance:
Specific endurance can be differ from sports to sports. Every sport has their own intensity. For example, marathon runners have to run long hours beside boxers have to complete their bout in 3 minute round.
Question 3.
Elucidate the term short term endurance and middle term endurance.
Answer:
1. Short Term Endurance:
Exercises for short distance can be fixed with the rest interval of short duration. It lasts upto 2 minutes and also called anaerobic activities. Short term endurance is required to resist fatigue in sports activities such as sprints and middle distance races.
2. Middle Term Endurance:
It can be required for such activities which lasts from 2 to 10 min. Middle term endurance depends on muscle endurance and speed endurance Middle distance races are the example of the middle term endurance (800 m, 1500 m) etc.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you know about coordination ability?
Answer:
Coordination ability is the ability to perform smooth and accurate motor task, often involving the use of the sense organs and series of correlated muscular contraction that affect a range of joint and therefore relative limb and body position. It depends on the neuro¬muscular coordination of the body. The various elements of coordinative abilities are orientation ability, coupling, ability differentiation ability, reaction ability, balance ability, rhythm, ability and adaptation ability.
Question 5.
Differentiate between agility and speed.
Answer:
Speed is maximum rate at which a person is able to move his body over a specific distance. We can say that speed is the ability to move from one place to another in the shortest possible time.
Agility is the ability to move and change direction and position of the body quickly and effectively while under control. It requires quick reflexes, coordination, balance, speed, and correct response to the changing situation.
Question 6.
Briefly explain about the types of strength.
Answer:
As per the requirements in different sports settings the following classifications of the strength can be given:
1. Dynamic strength or isotonic strength
2. Static strength or isometric strength
1. Dynamic Strength or Isotonic Strength:
When the contraction results in the change of muscles length and the pressure remains same throughout the contraction, it can be called dynamic strength. For example, involving movement at more than one joint i.e. push ups, pull- ups, barbell press, squats, lunges and dead lifts etc. Dynamic strength can also be divided in three parts:
(a) Maximum Strength:
It is the greatest strength that can be achieved voluntarily against a resistance. We can also define maximum strength as the amount of muscuo skeletal force a person can generate with all-out efforts..
(b) Explosive Strength:
It is the combination of speed and strength. It is the ability to overcome resistance with high speed. Explosive strength can be seen in sprint races, weight lifting, hammer throw, long jump and high jump etc.
(c) Strength endurance:
It is the combination of strength and endurance. It is the ability to overcome resistance for a longer duration. Long distance races, swimming and cycling are the examples of strength endurance.
2. Static strength or Isometric strength:
It is the ability of muscles to act against resistance without changing or shortening the length, e.g. Pushing against wall in which muscles develops tension without changing its length.
![]()
Question 7.
What do you know about flexibility? Give its types also.
Answer:
Flexibility is the range of movement possible around a joint. In general terms, flexibility has been defined as the range of motion around a joint and its surrounding muscles during passive movements.
Types of Flexibility
1. Static Flexibility: It is the ability to extend various joints in a stationary position.
(a) Passive Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with wider range and some external helps. For example, stretching exercise with the help of a partner.
(b) Active Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform flexibility or extension movements with larger amplitude without any external help or a partner. For example, swinging of legs.
2. Dynamic Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with greater amplitude when the body is in motion. Dynamic flexibility is more specific to sports to sports movements. For example, running and somersault in gymanastics or diving in swimming etc.
Question 8.
Enlist various types of speed.
Answer:
1. Reaction Speed: It is the ability to give a quick reaction on a signal. The sportsperson respond against the situation demand.
2. Acceleration Speed:
It is the ability to achieve maximum speed from stationary position. We can see it in sprints. Indirectly ,this ability depends on the other factors like explosive strength, technique and flexibility.
3. Movement Speed:
It is the ability to do maximum movement in minimum time. These can be seen in team games, combative sports, racket sports, throws and gymnastics etc.
4. Locomotor Ability:
This is the ability to maintain the speed after accelerated maximally. This can be seen in few events only i.e. 100 m, 200 m and 400 m etc.
5. Speed Endurance: It is the ability to maintain near maximal speed for a longer duration.
![]()
Question 9.
Highlight any three factors affecting physical fitness.
Answer:
1. Life Style:
A person who follow good life style are more fit and perform better in physical performance. Life style does not mean luxuries living; it means living with good habits. An individual who is habitual of smoking, liquor, drug etc. cannot perform well on these components of physical fitness. It affects physical fitness and overall health of a person.
2. Good Posture:
Postural deformities always creates hindrance in physical fitness, for example muscle imbalance, pain, nutrition deficiency, lordosis, scoliosis, round shoulder, knock knees etc. can affect physical fitness of a person, e.g. A person with flat feet would not be able to perform better in events demanding speed.
3. Diet:
Diet plays a major role in physical performance and it is required to maintain physical fitness level. Right amount of calories and nutrition will help athlete to perform their best. Without adequate carbohydrate and fluid, an athlete gets tired very easily and quickly. Protein is needed to rebuild muscles. Without carbohydrates, protein, vitamins athlete will not perform well and it also decreases physical fitness.
Question 10.
Differentiate between locomotor ability and reaction ability?
Answer:
Reaction Ability.
It is the ability of an individual to respond quickly to a given signal and perform the movement in well directed maimer. For example, in 100 m sprint when an athlete gets the signal he reacts quickly and performs the movement in desired direction.
Locomotor Ability:
This is the ability to maintain the speed after accelerated maximally. This can be seen in few events such as short distance races, i.e. 100 m, 200 m and 400 m etc.
![]()
Five Marks Question-Answers
Question 1.
Write the basic components of physical fitness strength and speed.
Answer:
Strength is defined as the force exerted by muscles groups during a single maximal muscle contraction. Strength can be developed with the right kind and amount of training.
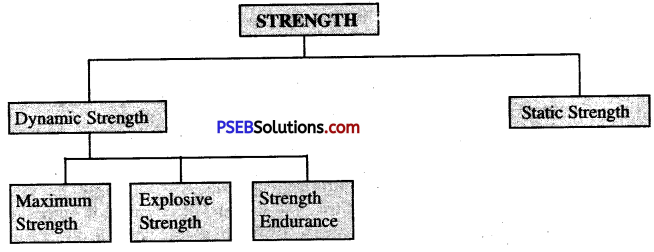
Types of Strength
As per the requirements in different sports settings the following classifications of the strength can be given:
1. Dynamic strength or isotonic strength
2. Static strength or isometric strength
1. Dynamic Strength or Isotonic Strength:
When the contraction results in the change of muscles length and the pressure remains same throughout the contraction, it can be called dynamic strength. For example, involving movement at more than one joint i.e. push ups, pull- ups, barbell press, squats, lunges and dead lifts etc. Dynamic strength can also be divided in three parts:
(a) Maximum Strength:
It is the greatest strength that can be achieved voluntarily against a resistance. We can also define maximum strength as the amount of muscuo skeletal force a person can generate with all-out efforts.
(b) Explosive Strength:
It is the combination of speed and strength. It is the ability to overcome resistance with high speed. Explosive strength can be seen in sprint races, weight lifting, hammer throw, long jump and high jump etc.
(c) Strength endurance:
It is the combination of strength and endurance. It is the ability to overcome resistance for a longer duration. Long distance races, swimming and cycling are the examples of strength endurance.
2. Static strength or Isometric strength:
It is the ability of muscles to act against resistance without changing or shortening the length, e.g. Pushing against wall in which muscles develops tension without changing its length.
Speed:
Speed is maximum rate at which a person is able to move his body over a specific distance. We can say that speed is the ability to move from one place to another in the shortest possible time.
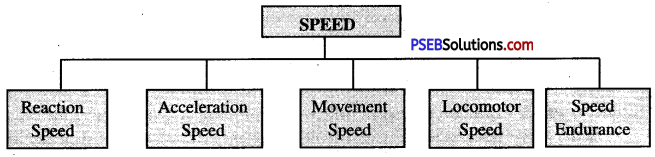 According to Barrow and McGee, “speed is the capacity of an individual to perform successive movement of the same pattern at a fast rate”. According to Johnson and Nelson, “speed is the rate at which a person can propel his body or parts of his body through space”.
According to Barrow and McGee, “speed is the capacity of an individual to perform successive movement of the same pattern at a fast rate”. According to Johnson and Nelson, “speed is the rate at which a person can propel his body or parts of his body through space”.
Speed comprises quick response, acceleration, maximum speed and speed endurance.
Types of Speed
1. Reaction Speed: It is the ability to give a quick reaction on a signal. The sportsperson respond against the situation demand.
2. Acceleration Speed:
It is the ability to achieve maximum speed from stationary position. We can see it in sprints. Indirectly ,this ability depends on the other factors like explosive strength, technique and flexibility.
3. Movement Speed:
It is the ability to do maximum movement in minimum time. These can be seen in team games, combative sports, racket sports, throws and gymnastics etc.
4. Locomotor Ability:
This is the ability to maintain the speed after accelerated maximally. This can be seen in few events only i.e. 100 m, 200 m and 400 m etc.
5. Speed Endurance: It is thejability to maintain near maximal speed for longer duration.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the importance of physical fitness.
Answer:
People who are physically fit are able to enjoy their life to the fullest. In today’s scenario of technological development people hardly spend time for their physical fitness. Now, question arises why it is important to be physically fit. The answer lies in the following points:
1. Improves Overall Health:
Physically fit persons possess numerous health advantages such as respiratory, cardiovascular health and overall functioning of the body remain in active state. This helps in reducing the chances of type 2 diabetes, heart diseases, reduces risk of some cancer and lastly helps in maintaining good health and wellness.
2. Weight Management:
As we all know that the person with over weight or obese people are more prone to health related problems such as high BP, Chotestrol level, diabetes etc. So, people who are living active lifestyle and physically fit are less likely to face these problems as they are able to control and manage their optimum weight with the help of regular exercise and stay fit.
3. Importance as a stress management:
Through the physical fitness and wellness programme, an individual become capable of managing stress, releiving stress and easily distracted from the daily stresses. Hence, this help in staying active and balanced in any stage of life. So, in order to maintain relaxed state of mind, a person should be physically fit.
4. Reduced risk of Injuries:
Physical fitness prevents the chances of injuries in later stage. The reason for the same could be the increased muscle strength, bone density, flexibility and stability. It reduces the chances of injuries especially, as a person get older e.g. strong bones mean less likely to suffer bone injuries as later age.
5. Increases life expectancy:
Regular exercise and physical acitivity reduces the chances of health related diseases, which increases life expectancy and reduce the risk of premature mortality. It has been observed that people who are more active tend to be healtheir and tend to live longer.
6. Proper growth and development:
Through fitness and wellness programme children tend to grow and develop better. They are able to attain good shape, height, structure and optimun weight with the help of their physical fitness programme. So, physically fit person are in well balanced state of their physical structure as well.
7. Improves work efficiency:
The person who are physically fit are tend to perform well in every sphere of life such as work place, family peer group etc. Due to their active and balance state of body and mind their output at work place is more and they tend to enjoy social group with more zeal and excitement. Hence, helps in enjoying their life to the fullest.
Hence, it can be concluded that physical fitness is important for the “Sound mind in a sound body”. To enjoy at every stage of life.
![]()
Question 3.
Briefly explain the factors affecting physical fitness.
Answer:
There are enormous factors which affects physical fitness in certain ways. Due to inactivity, both short term and long term physical fitness affected in number of ways. These factors which affect physical fitness are as ahead:
1. Anatomical Structure:
Anatomical/body structure of every individual is different or they have different shape and sizes. Inappropriate shape and size always hinder in physical performance. Sometimes, genetic impaired organ limits the physical performance of an individual, e.g. a person with smaller lower limbs have more balance as compare to vice-versa.
2. Physiological Structure:
Our all body system like respiratory system, circulatory system, muscular system and other body systems must work efficiently. Any malfunctioning in systems can affect the physical performance. Example would be problem in breathing or heart diseases etc. Hence, for the optimal physical fitness an individual must be physiological fit also.
3. Psychological Factor:
There are so many psychological disorders which has affect on physical performance e.g. stress, tension, anxiety etc. which are big barriers in performance. Mentally strong and stress free individual can be fit for sports. Stress and tension always limits the physical fitness of a person and hence, affects the performance.
4. Heredity and Environment:
Both, heredity and environment affects physical fitness of an individual. Heredity and environment interacts to produce their effects. This means that the way genes act depends on the environment in which they act. e.g. if any person is a good sportsman, the child tend to have some traits of physical domain. Similarly, environmental variables also effects an individual e.i., heighted Japanese and Americans.
5. Good Posture:
Postural deformities always creates hinderance in physical fitness, for example muscle imbalance, pain, nutrition deficiency, lordosis, scoliosis, round shoulder, knock knees etc. can affect physical fitness of a person, e.g. A person with flat feet would not be able to perform better in events demanding speed.
6. Diet:
Diet plays a major role in physical performance and it is required to maintain physical fitness level. Right amount of calories and nutrition will help athlete to perform their best. Without adequate carbohydrate and fluid, an athlete gets tired very easily and quickly. Protein is needed to rebuild muscles. Without carbohydrates, protein, vitamins athlete will not perform well and it also decreases physical fitness.
7. Life Style:
A person who follow good life style are more fit and perform better in physical performance. Life style does not mean luxuries living; it means living with good habits. An individual who is habitual of smoking, liquor, drug etc. cannot perform well on these components of physical fitness. It affects physical fitness and overall health of a person.
8. Climate:
Different climatic conditions always affects the physical fitness of a person. There are different climatic conditions like winter, summer, humid etc. which influence physical fitness. For better physical performance one must trained themselves in different climate conditions. For example if an individual belongs to the hot and humid area and they have to compete in cold area then, it affects their physical performance. To avoid these barriers one must practice in different climates.
9. Inactivity:
Lack of physical activity leads individual towards sedentary life style which also creates malfunctioning in body system. Physical activity is the term used to describe any kind of everyday activity where body’s movement bums calories. Example would be walking, running, cycling, swimming, sweeping or other household work. Due to inactivity body system gets weaken and other health issues arises.
10. Injury:
Injuries are part of sports. Lack of injury management can decrease performance as well as it affects psychologically on athletes mind. Severe or long term injuries often affecting more mentally then physically. Long term injuries leads to inactivity which ultimately affects the physical fitness of a person.
11. Age:
Age differences always affects physical fitness of an individual. As we cannot compare the physical efficiency of an adult with younger ones. In the same way when we grow older, our muscle mass decreases and body fat increases which really affects physical fitness.
12. Gender:
Gender plays a major role in physical performance. Both male and female have huge structural differences. For example female bodies are less muscular, but their joints are more flexible, which gives them greater range of motion and they have an advantage in sports such as gymnastics. Men have larger skeletal muscles as well as larger heart, which generate more power, strength, speed and endurance.
13. Healthy environment:
A healthy environment at school, home or at playfield is helpful in better physical health and fitness. It also encourages athlete to get best physical performance. A healthy environment and good participation is essential for proper growth and development which plays a key role in physical fitness.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain flexibility alongwith its various types?
Answer:
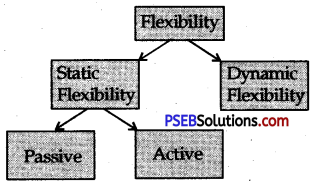
Flexibility:
Flexibility is the range of movement possible around a joint. In general terms, flexibility has been defined as the range of motion around a joint and its surrounding muscles.
Types of Flexibility:
1. Static Flexibility:
It is the ability to extend various joints in a stationary position.
(а) Passive Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with wider range and some external helps. For example, stretching exercise with the help of a partner. This flexibility is more then active flexibility,
(b) Active Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform flexibility or extension movements with larger amplitude without any external help or a partner. For example, swinging of legs.
2. Dynamic Flexibility:
It is the ability to perform extension movements around joints with greater amplitude when the body is in motion. Dynamic flexibility is more specific to sports to sports movements. For example, running and somersault in gymanastics or diving in swimming etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you know about coordination ability? Also explain various types of coordination ability.
Answer:
Coordinative ability is the ability to perform smooth and accurate motor task, often involving the use of the sense organs and series of correlated muscular contraction that affect a range of joint and therefore relative limb and body position. It depends on the neuromuscular coordination of the body.
Types of Coordinative Ability:
There are mainly seven types of coordinative abilities considered in sports. These are as follows:
1. Orientation Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to analyze and change his body position and its parts in time and space in relation to performance required. For example, gymnast changes his body position as per the requirements of sports performance and basket ball player changes his position from offense to defence as the ball possession goes to opponent.
2. Coupling Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to systematically and meaningfully combine the movement of different body parts for successful performance of sports movement. For example, during spiking in volleyball, the player jumps and hits the ball.
3. Differentiation Ability:
It is the ability which enables the sportsman to separate the different body position and its parts during execution of motor action with high accuracy and movement economy. For example, in volley ball when player jumps for spiking, but drops ball according to the situation.
4. Reaction Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to respond quickly to a given signal and perform the movement in well directed manner. For example, in 100 m sprint when an athlete gets the signal he reacts quickly and performs the movement in desired direction.
5. Balance Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to maintain the dynamic condition. For example, in 400 m race,, runner should run in his own lane.
6. Rhythm Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to understand the rhythm of movement and to execute the movement with required rhythm. For example, taking lay-up shot in basketball.
7. Adaptation Ability:
It is the ability of an individual to bring about an effective change in the movement according to anticipated change in the situation. For example, adaptation of scoop to the hitting a ball in hockey.
Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Physical Education Book Solutions Chapter 1 Physical Fitness Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.