Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Social Science Book Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
SST Guide for Class 7 PSEB Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Give answers to these questions in approximately 1-15 words.
Question 1.
What do you understand by natural vegetation?
Answer:
It means those herbs, trees and plants which grow on their own. Man has no contribution in it. The natural vegetation of some place depends upon the surface, types of soil, climate, etc.
Question 2.
In how many types natural vegetation can be divided?
Answer:
- Forest,
- Grasslands, and
- Thorny bushes.
Question 3.
Which are the goods we get from the forests?
Answer:
Many types of wood, cane, grass for making paper, gum, biroza, turpentine, the skin for dying leather, medical herbs, etc are received from forests.
Question 4.
How do the forests help us indirectly?
Answer:
- These take carbon dioxide from atmosphere and release oxygen.
- These are helpful in bringing rainfall and controlling the temperature.
- They stop floods and soil erosion.
- They help in the absorbtion of water by the earth.
- The forests stop the expansion of deserts and provide natural habitat to wildlife.
![]()
Question 5.
What will be the effect of the development of forests?
Answer:
There will be no wood and the world will become a big desert.
Question 6.
How man is disturbing the ecological balance?
Answer:
In order to make residential colonies and for obtaining agricultural land, man is deforesting, which is contributing towards damaging the ecological balance.
II. Answer the following questions in about 50-60 words.
Question 1.
Which are the forests that are economically useful? Explain.
Answer:
The most important and commercially valuable forests are coniferous forests. These forests are known as severgreen forests. In Eurasia these are known as Taiga forests. The trees found here are Cheerh, Fur, Spruce. We can get soft wood from these trees, which is used for making pulp and paper.
Question 2.
Why are the monsoon forests called deciduous forests?
Answer:
These forests are found on less heated latitudes. The areas which has more rainfall in any climate, there these trees have broad leaves. Such type of forests are more in those areas where there is more rainfall, because of monsoon winds. The season where there is no rainfall these trees shed their leaves. These forests are important from commercial point of view. Because these are less dense and within human reach. We get building wood and fuel wood from these forests, but most monsoon forests have been cut to give way for residential colonies and agriculture.
Question 3.
Write about the temperate grasslands.
Answer:
The hot and cold grasslands are found in hot and cold areas where the grass does not grow enough but it is soft and dense, so it is very useful for cattle grazing. In Eurasia these grasslands are called stepese, in North America these are called prairies, in South America-Pampas, in South Africa weld and in Australia these are known as Downs.
Question 4.
Write about the hot desert vegetation.
Answer:
Hot desert vegetation is found mainly in African Sahara and Kalahari, the deserts of Arab and Iran, the Thar desert of India-Pakistan. In South America Autocama, and in North America there is California desert and North Mexico desert and in Australia there is western Australian desert. Because of excess heat and very low rainfall there is very less vegetation. Here only thorny bushes, small herbs and grasses are born. The vegetation has been so made naturally that which can tolerate excess heat and dryness. The roots are long and thick. So that the plants can get moisture from the depth of earth. The bark of the plants is thick, the leaves are also thick and silky so that water is not wasted through vaporization.
Question 5.
Why is it necessary to conserve forests?
Answer:
The forests have a great role to play in our life, these fulfil our many needs. The wood from forests is used as fuel, building, paper making, railway sleepers as well as for cloth making. The forests-help to bring rainfall, control floods and soil erosion. But because of the increase in population the consumption of forests is increasing, so the area under forests is also decreasing. We must take care about planting more and more trees.
III. Things to do :
Question 1.
Prepare a list of various types of trees grown in your school compound. Plant a few sapplings also, with the help of your teacher.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
PSEB 7th Class Social Science Guide Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Which is an example of biosphere reserve of India?
(a) Corbett Park
(b) Kawal
(c) Pochmari
(d) Guindy.
Answer:
(c) Pochmari.
![]()
Question 2.
Which type of forest does sundari tree?
(a) Tropical evergreen
(b) Tropical thorn & scrubs
(c) Tropical deciduous
(d) Mangrove.
Answer:
(d) Mangrove.
Question 3.
What thing restricts the forests of tropical evergreen?
(a) Temperature
(b) Rainfall
(c) Air pressure
(d) Air current.
Answer:
(b) Rainfall.
Question 4.
A change in height also changes the :
(a) Climate
(b) Natural vegetation
(c) Weather
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 5.
Which of the following type of forests called Taiga?
(a) Coniferous
(b) Tropical
(c) Temperate
(d) Deciduous.
Answer:
(d) Deciduous.
Fill in the Blanks :
Question 1.
There is variation in ______ from one area to another due to temperature and moisture variations.
Answer:
Vegetation
![]()
Question 2.
In the ______ forests monkey and langoor are found.
Answer:
Tropical, Deciduous
Question 3.
The ______ forests are found between 10°N to 10°S Latitudes.
Answer:
Equatorial
Question 4.
National park covers a ______ area.
Answer:
Large
Question 5.
______ and continents in a combined form are called Eurasia.
Answer:
Europe, Asia.
True / False :
Question 1.
Coniferous forests are dominated by softwood trees.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Temperate grasslands are level and plains.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
Taiga forests are conical in shape.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Praries is in South Africa.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Some plants have very long roots to reach the underground water.
Answer:
True.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which are the industries dependent upon the forest wood?
Answer:
Many industries are dependent upon forest wood. These include furniture, sports goods, ships, railway bogeys, paper, plywood, packing boxes, etc.
Question 2.
What are the three factors which affect the varieties of forests?
Answer:
- Rainfall,
- Climatic conditions,
- Temperature.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Eurasia?
Answer:
European and Asian continents in a combined form are called Eurasia.
Question 4.
Where is forest wood used mainly?
Answer:
Mainly it is used as fuel i.e. 50%, 33% is used in building, construction and the balance is in other works.
Question 5.
Write some steps for the protection and care of forests.
Answer:
- Care should be taken that the forest should not catch fire.
- Deforestation should be followed in a limited manner. Along side there should be afforestation also.
- The various types of pests and diseases should be removed so as not to destroy the forests.
- More and more trees should be planted around canals, ponds, rivers, roads and railway lines.
- There should be less use of wood for fuel purpose. Instead we should use sun energy and cow dung gas.
- Even in building, instead of wood there should be the use of some alternative material.
Question 6.
Mention the uses of coniferous forests.
Answer:
Coniferous forests are dominated by softwood trees. These woods are very useful for making pulp, which is used in the making of paper and newsprint. Match boxes and packing boxes are also made from softwood.
Question 7.
Why the tropical evergreen forests in Brazil are called lungs of the earth?
Answer:
The tropical evergreen forests in Brazil are so extensive that they produce enough oxygen which can be used by the living beings.
Question 8.
List some typical animals lives in the Tropical rain forest.
Answer:
Anaconda, monkey, lemurs, apes, lizards and some kind of frogs are typical to tropical rain forest.
![]()
Question 9.
Name the local names of Tropical Grasslands.
Answer:
In Africa these are known as parkland, in Venezuela these are known as Laoess and in Brazil these are known as Pampas.
Question 10.
Write about the vegetation of Cold desert.
Answer:
In cold deserts when the snow melts for a short time some small flowery plants take root. In the northern parts grass like moss and Lichen grow.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why the equatorial forests are considered a skyscraper?
Answer:
Skyscraper means a very high rising multi-storey building. The equatorial forests also represent such a kind of scheme that is why equatorial forest are called skyscrapers :
- The uppermost storey is made up of 70m. high trees. Here sun and air both are available. We get both fruit and flower here.
- The storey under this is umbrella-shape. The branches of the trees get entangled and take the form of umbrella type roof. Here the sunlight is less.
- The lower most storey has branches which rise on the trees and get entangled with each other. The branches which cannot live without sunlight move upwards to get sunlight.
- At the lowest level, there is extreme darkness, there is no sunlight. The leaves are damaged and smelly the area is full of insects and pests.
Question 2.
What is known as food-chain? State the status of humans in this food-chain.
Answer:
The feeding relationship between various organisms in an ecosystem is known as food-chain. Green plants use sun’s energy to produce their food. The plant food is eaten by animals. As a result transfer of sun’s energy also takes place. Some animals also eat plant eating animals. Thus energy is transferred to second trophic level. Humans are placed at the top in this food-chain. They eat both plant as well as plant eating animals.

Food Pyramid
![]()
Question 3.
Give a brief account of Equatorial Forests.
Answer:
These forests are found in those areas which receive over 200 cm of rainfall.
These are also known as tropical rain forests.
Location: These forests are found in the Amazon basin of South America, Zaire basin of Africa, South East Asian countries such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Myanmar, Thailand, New Guinea and Western ghats.
Main features:
- These trees have broad leaves and their wood is hard.
- The trees do not shed their leaves at any particular time of the year.
- The forest is thick and luxuriant with plenty of trees.
- Trees of same species are scattered in distribution.
Animal Life: Large animals like elephants and rhinoceros are found only in relatively less dense parts of these forests. On the other hand, the animals that can live on trees or in “the water bodies are more numerous. Jaguar, puma, monkey, squirrels and insects are common.
Question 4.
Explain the typical features of Thorny vegetation.
Answer:
Lack of water, dry winds and high temperature make conditions difficult for plants. However, plants do grow in the deserts and are admirably adapted to the environment.
Main features:
- The roots of some plants spread far and wide but just below the surface of the ground. They absorb the rain water before it soaks away underground. The roots also absorb the dew which forms on the ground at night.
- Some plants have very long roots to reach the underground water. The roots of the acacia may go down 30 m or more in search of water.
- The leaves are often shed or reduced and the plant becomes dormant and stops growing during the driest periods in order to survive.
- The leaves of many plants are tiny, waxy, leathery or varnished to minimize loss of water.
Wildlife: Animals survive the drought and heat at the desert’through adaptation. The typical animals are lizard, snake, camel, etc.
Question 5.
Give a brief description of Temperate Grasslands.
Answer:
Temperate grasslands are level, treeless plains. They lie far away from the influence of the sea. Temperate Grassland are known by different names in different continents.
- Pampas-Argentina
- Prairie-North America.
- Veld-South Africa
- Steppe-Central Asia
- Downs-Australia.
Main features :
- The rainfall is not sufficient for trees to grow. Some trees are found on hill sides with more rainfall, or along rivers. Willows and polar are the common trees.
- Short grass grows everywhere. Areas, where the rainfall is more than 50 cm, have a rich carpet of grass suitable for cattle rearing.
- Areas that receive less than 50 cm of rainfall have coarse grass which is suitable for grazing only sheep and goats.
- The appearance of the grassland varies with the season.
Wildlife: Rodents, such as the prairie dog of America the gerbil of Africa, the hamster of Eurasia and the widespread mole, retreat underground escape from predators and the summer heat.
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the main features of Taiga forests.
Answer:
- These forests are found in higher latitudes. (50°-70° N)
- These are coniferous forests.
- These are conical in shape.
- These are tall softwood evergreen trees.
- These trees are useful for making pulp for newsprint and paper.
- Matchbox and packing boxes are made from these.
- Chir, pine, cedar, are important trees.
- Silver fox, mink, polar bear are common animals.
Question 7.
Write about the equatorial type of forest.
Answer:
The equatorial forests are found between 10° north and 10° south latitude. These forests are known as evergreen dense forests. On the equator there is high temperature the whole year and there, is more rainfall also. That is why dense forests are found here. The upper branches of these trees are combined in such a manner that these look like an umbrella. Even the sunlight cannot reach earth. There are many types of trees in these forests. Still these trees are not commercially profitable. The reason is that these forests are so dense that it is not possible to cut these off. South America, middle of Africa, south-east Asia and Medagaskar have big areas under these kinds of forests. In Australia and middle America these forests have covered smaller area. In South America-Brazil such forests are known as Selwas in Amazon Basin.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write in detail about the natural vegetation. :
Answer:
Natural Vegetation. It means those herbs, trees and plants which grow on their own. Man has no contribution on it. The natural vegetation of some place depends upon the surface, types of soil, climate, etc.
Parts of Natural Vegetation.
- Forest
- Grasslands, and
- Thorny bushes.
Detailed Description:
1. Forests: Forests are affected by quantity of rainfall, climatic distribution, temperature, etc. This type of vegetation is of three types:
1. Equatorial Forests: The equatorial forests are found between 10° north and 100 south latitude. These forests are known as evergreen dense forests.
On the equator there is high temperature the whole year and there is more rainfall also. That is why dense forests are found here. The upper branches of these trees are combined in such a manner that these look like an umbrella.
Even the sunlight cannot reach earth. There are many types of trees in these forests. Still these trees are not commercially profitable. The reason is that these forests are so dense that it is not possible to cut these off. South America middle of Africa, south-east Asia and Medagaskar have big areas under these kind of forests. In Australia and middle America these forests have covered smaller area. In South America-Brazil such forests are known as Selwas in Amazon Basin.
2. Monsoon Forests. These forests are found on less heated latitudes. The areas which has more rainfall in any climate, there these trees have broad leaves. Such type of forests are more in those areas where there is more rainfall, because of monsoon winds. The season where there is no rainfall these trees shed their leaves. These forests are important from commercial point of view. Because these are less dense and within human reach. We get building wood and fuel wood from these forests, but most monsoon forests have been cut to give way for residential colonies and agriculture.
3. Coniferous Forests. The most important and commercially valuable forests are coniferous forests. These forests are known as evergreen forests. In Eurasia these are known as Taiga forests. The trees found here are Cheerh, Fur, Spruce. We can get soft wood from these trees, which is used for making pulp and paper.
2. Grasslands. The hot and cold grasslands are found in hot and cold areas where the grass does not grow enough but it is soft and dense, so it is very useful for cattle grazing. In Eurasia these grasslands are called stepese, in North America these are called prairies, in South America—Pampas, in South Africa weld and in Australia these are known as Downs.
3. Thorny Bushes. Hot desert vegetation is found mainly in African Sahara and Kalahari, the deserts of Arab and Iran, the Thar desert of India-Pakistan. In South America Atacama, and in North America there is California desert and North Mexico desert and in Australia there is western Australian desert. Because of excess heat and very low rainfall there is very less vegetation. Here only thorny bushes, small herbs and grasses are born. The vegetation has been so made naturally that which can tolerate excess heat and dryness. The roots are long and thick. So that the plants can get moisture from the depth of earth. The bark of the plants is thick, the leaves are also thick and silky so that water is not wasted through vaporization.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about the care and protection of wild animals. Describe the role of wild animals in ecological balance.
Or
What is the role of wildlife in maintaining ecological balance?
Answer:
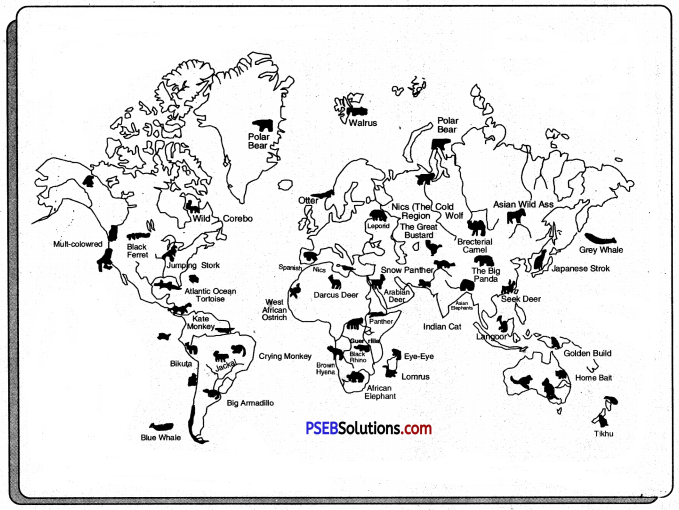
Conservation of Wildlife. India is rich in wildlife. There are about 81,000 known species of animals. She has 2500 species of fish and 1200 species of birds. But many of these species have been destroyed by man. Many rare species have become extinct in India. Our rich wildlife is a rich heritage formed through centuries. It must be preserved. Many of the species are found only in India such as swamp deer, the one- homed rhinoceros, Kashmir stag, Nilgai, etc. These rare species are in danger of extinction. Wildlife Act provides for the protection and conservation of these species. For this, zoos, national parks, bio-reserves and tiger reserves have been established in India.
The wildlife week is celebrated in the first week of October.
Difference between National Park and Sanctuaries
| National Park | Govt. Sanctuaries |
| 1. A national park is a reserved area meant for preserving natural vegetation, wildlife and natural beauty. | 1. A Govt, sanctuary is a reserved area meant for the preservation and development of endangered species. |
| 2. It covers a large area. | 2. It covers a small area. |
| 3. Corbett National Park is an example. | 3. Kaziranga Sanctuary is an example. |
Extinction of certain species of animals and birds: Various kinds of animals and birds are found in the Indian forests. Important among them are the elephants, tigers, leopards, lions, rhinoceros, deer, etc. Several species of animals have become extinct in our country due to their reckless hunting and clearing of forests. As a result, rhinoceros, leopards, lions must deer and the Great Indian Bustard are found only in a small number. We should preserve these precious assets of our country.
Protection of Wildlife: The ways to preserve wildlife are as follows :
- We should not fall trees thoughtlessly so that the wildlife population may get shelter and increase in the forests.
- We should not hunt animals and birds in the mating season.
- There should be a total ban on the hunting of rare species of wild animals so that they may not get extinct.
- We should co-operate with the government in its efforts to preserve wildlife.