Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In \(\mathrm{PO}_{4}^{3-}\) ion formal charge on the oxygen atom of P—O bond is
Answer:
In \(\mathrm{PO}_{4}^{3-}\) ion, formal charge on each O-atom of P—O bond
= \(\frac{\text { total charge }}{\text { Number of O-atoms }}=-\frac{3}{4}\) = -0.75
Question 2.
Which of the following molecules show super octet?
CO2, CIF3, SO2, IF5
Answer:
ClF3 and IF5 are super octet molecules.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following has highest lattice energy and why?
CsF, CsCl, CsBr, Csl
Answer:
CsF has highest lattice energy because ‘F’ is smallest in size and is more electronegative, therefore, it has maximum ionic character and maximum force of attraction, hence, highest lattice energy.
Question 4.
Account for the following:
The experimentally determined N—F bond length in NF3 is greater than the sum of the single covalent radii of N and F.
Answer:
This is because both N and F are small and hence, have high electron density. So, they repel the bond pairs thereby making the N—F bond length larger.
Question 5.
What is valence bond approach for the formation of covalent * bond?
Answer:
A covalent bond is formed by the overlapping of half-filled atomic orbitals.
Question 6.
Why axial bonds of PCI5 are longer than equatorial bonds?
Answer:
This is due to greater repulsion on the axial bond pairs by the equatorial bond pairs of electrons.
Question 7.
Which type of atomic orbitals can overlap to form molecular orbitals?
Answer:
Atomic orbitals with comparable energies and proper orientation can overlap to form molecular orbitals.
Question 8.
Why KHF2 exists but KHCl2 does not?
Answer:
Due to H-bonding in HF, we have
![]()
![]()
This can dissociate to give \(\mathrm{HF}_{2}^{-}\) ion and hence, KHF2 exists but there is no H-bonding in H-Cl. So, \(\mathrm{HCl}_{2}^{-}\) ion does not exist and hence, KHCl2 also does not exist.
Question 9.
How many nodal planes are present in n(2px) and n(2px) molecular orbitals?
Answer:
One and two respectively.
Question 10.
What is the magnetic character of the anion of K02?
Answer:
Anion of KO2 is \(\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}\) (superoxide ion) which has one unpaired electron and hence is paramagnetic.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the change in hybridisation (if any) of the Al-atom in
the following reaction:
AlCl3 + Cl– → \(\mathrm{AlCl}_{\mathbf{4}}^{-}\)
Answer:
Electronic configuration of Al in ground state,
13Al = 1s2, 2s2,2p6,3s2,3p1x
In excited state = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1, 3p1x, 3p1y
In the formation of AlCl3, Al undergoes sp2 hybridisation and it is trigonal
planar in shape. While in the formation of AlCl4–, Al undergoes sp3
hybridisation.
It means empty 3Pz orbital also involved in hybridisation.
Thus, the shape of AlCl4– ion is tetrahedral.
Question 2.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing bond angle, with appropriate reason
\(\mathrm{NO}_{2}, \mathrm{NO}_{2}^{+}, \mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\)
Answer:
\(\mathrm{NO}_{2}, \mathrm{NO}_{2}^{+}, \mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\). This is because \(\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{+}\) has no lone pair of electrons
(i.e., has only bond pairs on two sides) and hence it is linear.
NO2 has one unshared electron while \(\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\) has one unshared electron pair. There are greater repulsion on N—O bonds in case of \(\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\) than in case of NO2
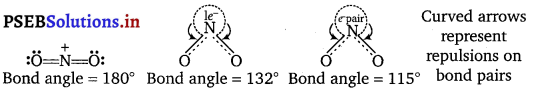
Question 3.
Among the molecules, \(\mathbf{O}_{2}^{-}, \mathbf{N}_{2}^{+}, \mathrm{CN}^{-}\) and \(\mathbf{O}_{2}^{+}\) identify the species which is isoelectronic with CO.
Answer:
Isoelectronics species are those species which have the same number of electrons. CO in total has 14 electrons (6 from carbon and 8 from oxygen). Out of the given ions CN is the ion which has 14 electrons (6 from carbon 7 from Nitrogen and 1 from the negative charge). Thus CN– ion is isoelectronic with CO.
![]()
Question 4.
Which is more polar : COa or N20? Give reason.
Answer:
N2Ois more polar than CO2. This is because CO2 is linear and symmetrical.
Its net dipole moment is zero im
on the other hand, is linear but unsymmetrical. It is considered as a resonance hybrid of the following two structures
![]()
It.has a net dipole moment of 0.116 D.
Question 5.
Aluminium forms the ion Al3+, but not Al4+ why?
Answer:
Aluminium [Ne]3s2 3p1 can achieve the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas (Ne) by losing only three electrons. : Al3+ = 1s2 2s2 2p6.
Aluminium will not form Al4+ ion because an extremely high amount of energy would be required to remove an electron from the stable noble gas configuration.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
On the basis of VSEPR theory, predict the shapes of the following
(i) \(\mathbf{N H}_{2}^{-}\) (ii) O3
Answer:
(i) Shape of \(\mathbf{N H}_{2}^{-}\)
Number of valence electrons on central N atom = 5 + 1 (due to one unit negative charge) = 6
Number of atoms linked to it = 2
∴ Total number of electron pairs around N
= \(\frac{6+2}{2}\) = 4 and number of bond pairs = 2
∴ Number of lone pairs = 4 —2 = 2. Thus, the ion is of the type AB2E2
Hence, it has bent shape (V-shape).
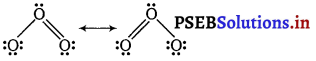
(ii) Shape of O3
While predicting geometry of molecules containing the double (or multiple) bond is considered as one electron pair, e.g., in case of ozone, its two resonating structures are
![]()
Thus, the central O-atom is considered to have two bond pairs and one lone pair, i.e., it is of the type AB2E. Hence, it is a bent molecule. Thus, the two resonating structures will be
Question 2.
In each of the following pairs of compounds, which one is more covalent and why?
(i) AgCl, Agl
(ii) BeCl2,MgCl2
(iii) SnCl2, SnCl4
(iv) CuO, CuS
Answer:
Applying Fajans’ rules, the result can be obtained in each case as follows :
(i) Agl is more covalent than AgCl. This is because I– ion is larger in size than Cl– ion and hence is more polarised than Cl– ion.
(ii) BeCl2 is more covalent thanMgCl2. This is because Be2+ ion is smaller in size than Mg2 ion and hence has the greater polarising power.
(iii) SnCl4 is more covalent than SnCl2. This is because Sn4+ ion has greater charge and smaller size than Sn2+ ion and hence has greater polarising power.
(iv) CuS is more covalent than CuO. This is because S2- ion has larger size
than O2- ion and hence is more polarised than O2- ion.