Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Agriculture Book Solutions Chapter 1 Soil and Soil Management Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Agriculture Chapter 1 Soil and Soil Management
Agriculture Guide for Class 8 PSEB Soil and Soil Management Textbook Questions and Answers
(A) Answer in one to two words:
Question 1.
What is the pH of normal soil for crop production?
Answer:
pH should be from 6.5 to 8.7.
Question 2.
Name any two physical properties of soils.
Answer:
Particle size, soil density, pore size, water holding capacity etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Which soils have highest infiltration rate?
Answer:
Sandy soil.
Question 4.
What is the percentage of clay particles in clayey soils?
Answer:
At least 40% clayey particles.
Question 5.
Which soil property determines the soil acidity or alkalinity?
Answer:
Value of pH for the soil.
Question 6.
Which are the prominent salts present in saline soils?
Answer:
Chlorides and sulphates of potassium, calcium and magnesium.
Question 7.
The soil with higher concentration of sodium carbonates and bicarbonates are categorized as.
Answer:
Alkali soil.
![]()
Question 8.
Which amendment is used for reclamation of alkali soils?
Answer:
Gypsum.
Question 9.
Name two green manure crops.
Answer:
Daincha, Jantar.
Question 10.
Which crop is best suited for cultivation in clayey soils?
Answer:
For cultivation of paddy crop.
![]()
(B) Answer in one to two sentences:
Question 1.
What is soil?
Answer:
Soil is the upper layer of earth in which plant roots grow, plants take water and nutrients from it.
Question 2.
Write the important functions of soil.
Answer:
Crops absorb water and nutrients from soil and soil also gives physical strength to the plants.
Question 3.
Enlist the physical properties of soil.
Answer:
Size of particles, soil density, pore size, water holding capacity etc.
Question 4.
Compare clayey and sandy soils.
Answer:
| Sandy Soil | Clayey Soil |
| 1. If soil is rubbed between finger and thumb, it feels gritty. | 1. Soil particles are very fine. |
| 2. Water holding capacity in not good. | 2. Water holding capacity is large. |
| 3. Pore size is big. | 3. Pore size is very small. |
![]()
Question 5.
What acidic 90?
Answer:
Those soils which have high acidic content and their pH value is less than 7 are acidic soils. These soils are found in areas of heavy rain fall, due to this, bases drin out and due to decay of organic malter Like leaves etc. soil becomes acidic.
Question 6.
What is saline soil?
Answer:
Soils which have high content of salt in them are saline soils. These soils have chlorides and sulphates of potassium,, calcium and magnesium. .
Question 7.
Write two main methods to identify a sandy soil.
Answer:
- Sandy soils have higher infiltration rate.
- It feels gritty when soil is rubbed in hands.
- Moist ball breaks very easily.
Question 8.
What are the major properties of loamy soils?
Answer:
- Particles are very-very fine.
- Pore size is very small.
- When taken in hand it feels like powder.
- Water holding capacity is high.
Question 9.
What are saline-alkali soils?
Answer:
Soils with higher concentration of sodium and soluble salts in it are called saline-alkali soils.
Question 10.
What is puddling?
Answer:
Ploughing in flooded field is known as puddling.
![]()
(C) Answer in five to six sentences:
Question 1.
Describe the different types of sods according to their physical properties.
Answer:
Physical properties of soil are: size of soil particle, pore size, soil structure, water holding capacity etc. There are three types of soils:
1. Clayey Soil:
It has more than 40% of clay content. Its water holding capacity is high. Balls can be made from moist clay and do not break on applying pressure. Particles are fine and pore size is also very fine.
2. Sandy Soil:
These soils have low water holding capacity. Particle size is not very small and pore size is also not very small as compared to clayey soil, water infiltration rate is high. Moist ball break easily with very little pressure. When rubbed in hands it feels gritty.
3. Loamy soil:
Properties of this soil lies between sandy and clayey soil. Its properties are optimum for crop cultivation and is best suited for agriculture.
Question 2.
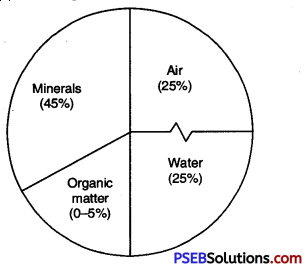
Give the diagrammatic representation of soil components.
Answer:
Soil is a mixture of minerals, organic matter, water and air. Their proportion is shown in the diagram below. Water and air content can vary.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the management practices for improving sandy soils.
Answer:
- Incorporate green manure which is 45-50 days old or before the flowering sets. Sunhemp/dhaincha can be used for this purpose.
- Apply well decomposed organic manue (FYM etc.) by ploughing.
- Poultry manure, pig manure and compost etc. can be mixed with the soil.
- Cultivate leguminous crops in such soils.
- Use small plot size for irrigation.
- Remove the top sandy layer by using Karaha.
- Incorporate clay soil or village pond soil to improve the quality.
Question 4.
Explain the method of reclamation of alkali soil.
Answer:
- Level the field uniformly so that distribution of water is same throughout the field.
- Do not allow the outflow of salt dissolved water to adjoining fields, prevent it by making strong bunds around the field.
- To know the requirement of gypsum for the soil, get soil and water tested.
- Broadcast the required dose of gypsum in the field and mix it with shallow ploughing.
- Apply green manure, organic manure etc. to improve the soil.
Question 5.
Explain in detail the management strategy for clayey soils.
Answer:
- To improve water infiltration rate and aeration of the clayey soil apply green manure and organic manure.
- Plough the crop residue in the soil.
- Plough the field at proper moisture content to avoid the formation of large-sized clods. .
- This soil is suitable for cultivation of paddy.
- There should be proper drainage system so as to drain out excessive water.
![]()
PSEB 8th Class Agriculture Guide Soil and Soil Management Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Is earth living or non-living according to soil scientists?
Answer:
It is living.
Question 2.
What is the percentage of minerals and organic matter in earth?
Answer:
Minerals 45% and organic matter 0-5%.
Question 3.
Which soil is called light soil?
Answer:
Sandy soil.
Question 4.
Which soil has high water holding capacity?
Answer:
Clayey soil.
Question 5.
Which soil is best suited for agriculture?
Answer:
Loamy soil.
Question 6.
Where is the problem of acidic soils found?
Answer:
In areas of heavy rainfall.
![]()
Question 7.
What is value of pH for Acidic soils?
Answer:
Less than 7.
Question 8.
What range of pH value is suited for agriculture?
Answer:
6.5 to 8.7.
Question 9.
What is pH of saline soils?
Answer:
Less than 8.7.
Question 10.
Which soils are called Kauai, reh, Thur or shorn?
Answer:
Saline soils.
Question 11.
How much is the water holding capacity of alkali soils?
Answer:
Very less.
Question 12.
Name a crop used for green manure?
Answer:
Sunhemp, Jantar.
Question 13.
What should be the plot size for sandy soils for irrigation?
Answer:
Small size.
Question 14.
What is the suitable time to mix lime in acidic soil?
Answer:
3-6 months before sowing the crop.
![]()
Question 15.
How big is the problem of acidic soils in Punjab?
Answer:
There is no problem of acidic soils in Punjab.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write reason why soils become acidic?
Answer:
Heavy rainfall helps in the growth of plants and more vegetation is found in such areas. Leaves etc. fall on the ground decompose and increase the acidic content. Rain water helps in the flowing out of basic salts which further adds to the acidic nature.
Question 2.
Write two properties of saline soils.
Answer:
- Chloride and sulphate salts of calcium, magnesium and potassium have high concentration in such soils.
- pH of these soils is less than 8.7.
Question 3.
Write two properties of alkali soils.
Answer:
- In such soils concentration of carbonates and bicarbonates of sodium is high.
- Infiltration rate of such soils is low.
Question 4.
Write two methods to reclaim the acidic soils.
Answer:
The soil is reclaimed by using lime. Remains from cane mill and wood ash can also be used.
![]()
Question 5.
Give properties of loamy soil.
Answer:
Its properties are between sandy and clayey soil. It feels like powder when taken in hands.
Question 6.
What is the meaning of water logged soil?
Answer:
Those soils in which water table is at depth of 0 to 1.5 m below surface of soil are called water logged soils.
Question 7.
How saline soils are reclaimed?
Answer:
Salts are washed away with water from the soil. For doing this field is flooded with water and is then ploughed. This water is drained out from the field which have salts dissolved in it. In another method, salts are made to dissolve into water and this water is allowed to leach down.
Question 8.
How can we improve sandy soils?
Answer:
We can improve sandy soil by incorporating 45-50 days old green manure crop of dhaincha/sunhemp in the soil.
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Make a list of physical properties of soil. Write few lines about any one of these?
Answer:
Different soils have different physical properties. Some of the physical properties are:
- Particle size
- Depth
- Colour
- Density
- Water holding capacity
- Temperature
- Pore size
- Infiltration rate
Particle size:
Soil is made up of different mineral particles. Particle size depends on the ratio in which different sized particles are present in the soil. Fertility of the soil depends on particle size to some extent.
Question 2.
What is pH value? What is the effect of pH value on soil?
Answer:
pH value:
pH value tells us the nature of the soil i.e. acidic, neutral or alkaline nature. pH value is the ratio of concentration of hydrogen ion (H+) and hydroxyl ion (OH-) in a solution.
| pH value of soil | Type of soil |
| > 8.7 | Alkali |
| 8.7 – 7 | slightly alkaline |
| 7 | Neutral |
| 7.6 to 5 | light acidic |
| < 6.5 | acidic |
Question 3.
Write briefly about the chemical characters of soil?
Answer:
Soils have different types of chemical properties like pH, electric conductivity (EC), salt content, etc. Based on these chemical properties, soils are classified as below:
- Acidic soils: These soils have a pH value of less than 7. These soils are found in areas where high rainfall occurs.
- Salt-affected soils: These soils have a high concentration of salts. Based on salt concentration, pH and EC soils can be saline, alkali, or saline-alkali.