Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 12th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease
Very short answer type questions
Question 1.
Malaria, typhoid, pneumonia and amoebiasis are some of the human infectious diseases. Which ones of these are transmitted through mechanical carriers?
Answer:
Malaria and amoebiasis are transmitted through mechanical carriers.
Question 2.
How does haemozoin affect the human body when released in blood during malarial infection?
Answer:
Haemozoin is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days during malarial infection.
Question 3.
What causes swelling of the lower limbs in patients suffering from filariasis?
Answer:
Wuchereria (W. bancrofti and W. malayi).
![]()
Question 4.
Why is Gambusia introduced into drains and ponds?
Answer:
To feed on mosquito larvae so as to eliminate the vectors responsible for causing malaria.
Question 5.
Recently chikungunya cases were reported from various parts of the country. Name the vector responsible.
Answer:
Aedes mosquito is responsible for chikungunya cases.
Question 6.
What role do macrophages play in providing immunity to humans?
Answer:
Macrophages destroy the microbes (by phagocytosis) and provide protection against diseases.
Question 7.
In what way are monocytes a cellular barrier in immunity?
Answer:
Monocytes can phagocytose (by the process called phagocytosis) and thereby destroy the pathogens.
Question 8.
How does colostrum provides initial protection against diseases to new bom infants? Give one reason.
Answer:
Colostrum contains several antibodies which are absolutely essential for developing resistance in the new-born babies.
![]()
Question 9.
State the functions of mast cells in allergy response.
Answer:
Mast cells release chemicals like histamine and serotonin in allergic response.
Question 10.
What is an autoimmune disease? Give an example.
Answer:
It is an abnormal immune response in which the immune system of the body starts rejecting its own body cells or ‘self cells and molecules. For example, rheumatoid arthritis.
Question 11.
State two different roles of spleen in the human body.
Answer:
Spleen is the secondary lymphoid organ that stores lymphocytes, it filters microbes and acts as a reservoir to store erythrocytes.
Question 12.
Why sharing of injection needles between two individuals is not recommended?
Answer:
Sharing of needles can transmit diseases like HIV, AIDS, Hepatitis B or C from infected to non-infected individuals.
Question 13.
Retroviruses have no DNA. However, the DNA of the infected host cell does possess viral DNA. How is it possible?
Answer:
On infecting the host cell, the viral RNA transforms into viral DNA by reverse transcription. This viral DNA then incorporates into the host DNA.
Question 14.
Suggest any two techniques which can help in early detection of bacterial and viral infections much before the symptoms appear in the body.
Answer:
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
![]()
Question 15.
Mention the useful as well as the harmful drug obtained from the latex of Poppy plant.
Answer:
Useful drug – morphine.
Harmful drug – heroin.
Short answer type questions
Question 1.
Define the term health. Mention any two ways of maintaining it.
Answer:
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being. Good health can be maintained through balanced diet and regular exercise.
Question 2.
List the specific symptoms of typhoid. Name its causative agent.
Answer:
Specific symptoms of typhoid are as follows:
- Constant high fever (39° to 40°C)
- Weakness
- Stomach pain
- Loss of appetite
Its causative agent is Salmonella typhi.
Question 3.
Identify a, b, c and d in the following table:
| Name of the human disease | Name of the causal bacteria/virus | Specific organ or its part affected |
| (i) Typhoid | Salmonella typhi | a |
| (ii) Common cold | b | c |
| (iii) Pneumonia | Streptococcus pneumoniae | d |
Answer:
(a) Small intestine
(b) Rhino virus
(c) Nose and respiratoiy passage
(d) Alveoli of lungs
![]()
Question 4.
At what stage does Plasmodium gain entry into the human body? Write the different stages of its life-cycle in the human body.
Or Trace the life-cycle of malarial parasite in the human body when bitten by an infected female Anopheles.
Answer:
Plasmodium falciparum is the malarial parasite.
Plasmodium life-cycle:
The gametocyte develops in the red blood cells of human.
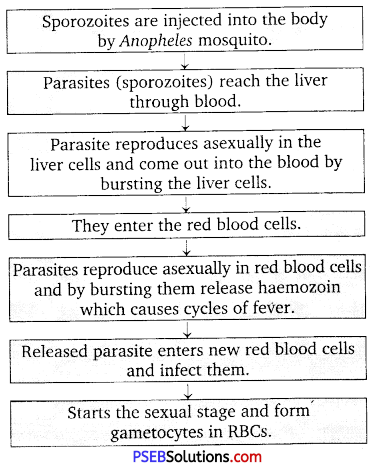
Question 5.
Explain the role of the following in providing defence against infection in human body :
(i) Histamines
(ii) Interferons
(iii) B-cells
Answer:
(i) Histamines: These are chemicals which cause inflammatory responses.
(ii) Interferons: These are glycoproteins which protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
(iii) B-cells: These produce proteins called antibodies in response to pathogens into the blood to fight with them.
Question 6.
(a) What is the functional difference between B cells and T cells?
(b) Name the source used to produce hepatitis-B vaccine using rDNA technology.
Answer:
(a)
| B-Lymphocytes | T-Lymphocytes |
| (i) They arise from bone marrow. | They arise from bone marrow and thymus. |
| (ii) B-cells form humoral or antibody-mediated immune system (AMIS). | T-cells form cell-mediated immune system (CMIS). |
| (iii) They defend against viruses and bacteria that enter the blood and lymph. | They defend against pathogens including protists and fungi that enter the cells. |
| (iv) They form plasma cells and memory cells by the division. | They form killer, helper and suppressor cells by the division of lymphoblasts. |
(b) Hepatitis-B vaccine is produced from surface antigens of transgenic yeast by r-DNA technology. The antigens represent whole protein vaccine.
![]()
Question 7.
In the metropolitan cities of India, many children are suffering from allergy/asthma. What are the main causes of this problem. Give some symptoms of allergic reactions. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Allergy is the exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment. In metropolitan cities life style is responsible in lowering of immunity and sensitivity to allergens. More polluted environment increases the chances of allergy in children. Some symptoms of allergic reactions are sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing.
Question 8.
Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Answer:
| Benign tumour | Malignant tumour |
| (i) It is a non-cancerous tumour. | It is a cancerous tumour. |
| (ii) Benign tumour does not show metastasis and is non-invasive. | It shows metastasis and thus invades other body parts. |
| (iii) It stops growth after reaching a certain size. | Malignant tumour shows indefinite growth. |
| (iv)Limited | There is no adherence amongst cells. They tend to slip past one another. |
| (v) It is less fatal to the body. | It is more fatal to the body. |
Question 9.
Write the source and the effect on the human body of the following drugs:
(i) Morphine
(ii) Cocaine
(iii) Marijuana
Answer:
(i) Morphine: It is obtained from poppy plant Papaver somniferum. It binds to specific opioid receptors present in central nervous system and ‘ gastrointestinal tract.
(ii) Cocaine: It is obtained from coca plant Erythroxylum coca. It interferes with the transport of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
(iii)Marijuana : It is obtained from Cannabis sativa. It affects the cardiovascular system of the body.
Question 10.
(a) Why is there a fear amongst the guardians that their adolescent wards may get trapped in drug/alcohol abuse?
(b) Explain ‘addiction’ and dependence’ in respect of drug/alcohol abuse in youth.
Answer:
(a) Reasons for alcohol abuse in adolescents:
- Social pressure
- Curiosity and need for adventure, excitement and experiment.
- To escape from stress, depression and frustration.
- To overcome hardships of life.
- Unstable or unsupportive family structure
(b) Addiction: The psychological attachment to certain effects such as euphoria and a temporary feeling of well-being, associated with drugs and alcohol is called addiction.
Dependence: The tendency of the body to manifest a characteristic and unpleasant withdrawal syndrome on abrupt discontinuation of regular dose of drug/alcohol is called dependence.
![]()
Long answer type questions
Question 1.
(a) Cancer is one of the most dreaded diseases of humans. Explain ‘Contact inhibition’ and ‘Metastasis’ with respect to the disease.
(b) Name the group of genes which have been identified in normal cells that could lead to cancer and how they do so?
(c) Name any two techniques which are useful to detect cancers of internal organs.
(d) Why are cancer patients often given a-interferon as part of the treatment?
Answer:
(a) Contact inhibition is the property of normal cells in which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth.
Metastasis is the property in which tumour cells reach distant sites in the body, through blood.
(b) Proto oncogenes or Cellular oncogenes.
These genes when activated under certain condition could lead to oncogenic transformation of the cells.
(c) Biopsy/radiography/CT/MRI
(d) a-interferon activates immune system and destroys the tumour.
Question 2.
Why do some adolescents start taking drugs? How can the situation be avoided? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Many factors are responsible for motivating youngsters towards alcohol or drugs. Curiosity, need for adventure and excitement, experimentation are the initial causes of motivation. Some youngsters start consuming drugs and alcohol in order to overcome negative emotions (such as stress, pressure, depression, frustration) and to excel in various fields. Several mediums like television, internet, newspaper, movies etc. are also responsible for promoting the idea of alcohol to the younger generation. Amongst these factors, reasons such as unstable and unsupportive family structures and peer pressure can also lead an individual to be dependant on drugs and alcohol.
Preventive measures against addiction of alcohol and drugs are as follows:
(a) Parents should motivate and try to increase the willpower of their child.
(b) Parents should educate their children about the ill-effects of alcohol. They should provide them with proper knowledge and counselling regarding the consequences of addiction to alcohol.
(c) It is the responsibility of the parent to discourage a child from experimenting with alcohol. Youngsters should be kept away from the company of friends who consume drugs.
(d) Children should be encouraged to devote their energy in other extra¬curricular and recreational activities.
(e) Proper professional and medical help should be provided to a child if sudden symptoms of depression and frustration are observed.
![]()
Question 3.
A person shows strong unusual hypersensitive reactions when exposed to certain substances present in the air, identify the condition. Name the cells responsible for such reactions. What precaution should be taken to avoid such reactions? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
The condition is called allergy. Mast cells are responsible for such reactions.
To avoid such reactions following precautions must be taken:
- Use of drugs like antihistamine, adrenalin and steroids quickly reduces the symptoms.
- Avoid contact with substances to which a person is hypersensitive.
Question 4.
What would happen to immune system, if thymus gland is removed from the body of a person? [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer:
Thymus is the primary lymphoid organ. In thymus gland, immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. If thymus gland is removed from the body of a person, his immune system becomes weak. As a result the person’s body becomes prone to infectious diseases.